Iranian university students lifestyle and health status survey: study profile
- PMID: 29270393
- PMCID: PMC5738704
- DOI: 10.1186/s40200-017-0329-z
Iranian university students lifestyle and health status survey: study profile
Abstract
Background: The physical health assessment of university students in Iran is a national large scale assessment examining health behaviors among tertiary education students. Understanding risky health behaviors which are the major sources of global mortality and morbidity in adulthood is the key objective of this assessment.
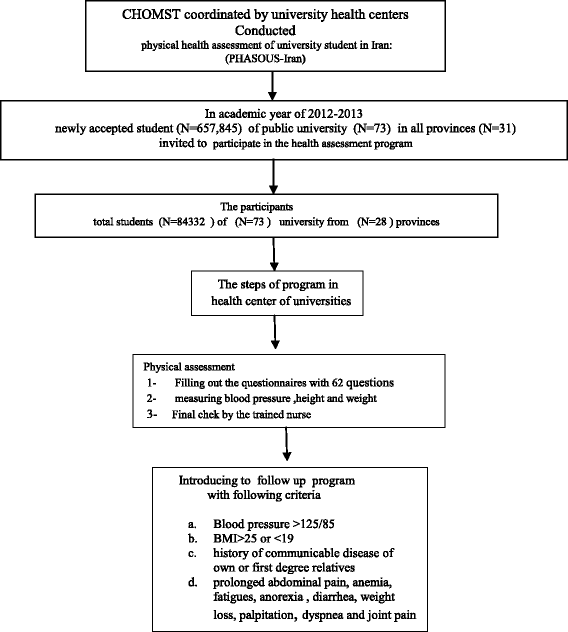
Methods: In academic year of 2012-2013, newly admitted students (N = 151,671) at 74 governmental eligible universities that had health center from 28 provinces were invited to participate in the health assessment program. The physical health behaviors of the students were evaluated by using questionnaire. The test-retest reliability method was applied to estimate the reliability of physical health questionnaire. After filling out the questionnaires, students were led to the examination room for the measurement of height, weight and blood pressure.
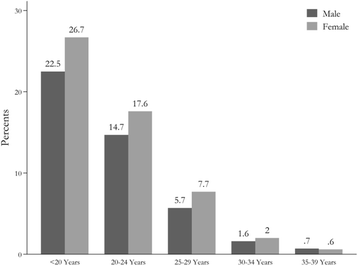
Results: From the total study population, 84,298 student's ages between 18 and 29 years old, were participated in the health assessment. The mean response proportion was 63%. The mean age of students was 21.5 ± 4.01, with 49.20% percent being <20 years old. 32.31% were between 20 and 24 years, 13.44% between 25 and 29 years, 69% of the participants were undergraduate 34.9% were master's students, and 2.9% were Ph.D. students. The mean BMI for total students was 22.5 ± 4.0 and regarding to gender, the mean BMI for male and female were 23.0 ± 4.1 and 22.2 ± 3.8 respectively.
Conclusion: Analysis of student's findings will generate multiple studies which report different aspects of physical health of Iranian university students who constitute a large proportion of young adult aged 18-29 years in the country. This assessment also provides opportunity to compare Iranian student's behavioral patterns with the behavioral pattern of students worldwide.
Keywords: Behavioral patterns; Physical health; Risky health behaviors; University students.
Conflict of interest statement
The assessment approved by the Counseling and health organization of the Ministry of Science and Technology etic committee. All participants signed consent forms.Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Organization WH . Adolescents: health risks and solutions, fact sheet N°345. 2014.
-
- Ann Hagell JCO. Young people’s health.Association for Young People Health’s. 2014.
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, Biryukov S, Abbafati C, Abera SF. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

