A Phase 2, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Study of Fresolimumab in Patients With Steroid-Resistant Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 29270487
- PMCID: PMC5733825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2017.03.011
A Phase 2, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Study of Fresolimumab in Patients With Steroid-Resistant Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
Introduction: Steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (SR-FSGS) is a common glomerulopathy associated with nephrotic range proteinuria. Treatment goals are reduction in proteinuria, which can delay end-stage renal disease.
Methods: Patients with SR-FSGS were enrolled in a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial of fresolimumab, a monoclonal anti-transforming growth factor-β antibody, at 1 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg for 112 days, followed double-blind for 252 days (NCT01665391). The primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving partial (50% reduction) or complete (< 300 mg/g Cr) remission of proteinuria.
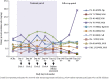
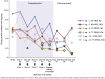
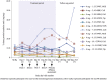
Results: Of 36 enrolled patients, 10, 14, and 12 patients received placebo, fresolimumab 1 mg/kg, and fresolimumab 4 mg/kg, respectively. The baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and urinary protein/creatinine ratio were 63 ml/min/1.73 m2 and 6190 mg/g, respectively. The study was closed before reaching its target of 88 randomized patients. None of the prespecified efficacy endpoints for proteinuria reduction were achieved; however, at day 112, the mean percent change in urinary protein/creatinine ratio (a secondary efficacy endpoint) was -18.5% (P = 0.008), +10.5% (P = 0.52), and +9.0% (P = 0.91) in patients treated with fresolimumab 1 mg/kg, fresolimumab 4 mg/kg, and placebo, respectively. There was a nonsignificant trend toward greater estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in the placebo group compared to either of the fresolimumab-treated arms up to day 252.
Discussion: The study was underpowered and did not meet the primary or secondary endpoints. However, fresolimumab was well tolerated and is appropriate for continued evaluation in larger studies with adequate power.
Keywords: fresolimumab; monoclonal antibody; proteinuria; steroid-resistant primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Figures




References
-
- D'Agati V.D., Kaskel F.J., Falk R.J. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2398–2411. - PubMed
-
- Korbet S.M. Clinical picture and outcome of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14(suppl 3):68–73. - PubMed
-
- Korbet S.M. Treatment of primary FSGS in adults. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1769–1776. - PubMed
-
- Ponticelli C., Rizzoni G., Edefonti A. A randomized trial of cyclosporine in steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1993;43:1377–1384. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

