Surgical outcomes of three different surgical techniques for treatment of convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia
- PMID: 29271419
- PMCID: PMC5898853
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2017.259
Surgical outcomes of three different surgical techniques for treatment of convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia
Abstract
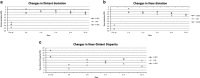
PurposeTo determine the outcomes of three different techniques of strabismus surgery in patients with convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia (CI-X(T)).Patients and methodsSixty-seven patients with CI-X(T) with near-distance disparity (NDD) ≥10 prism diopter (PD) were included in this 1-year follow-up prospective study and were randomly divided into three groups: slanted bilateral LR recession (S-BLR) group in which 22 patients underwent bilateral slanting recession of the lateral rectus (LR) muscle, the I-RR group with 23 patients who underwent improved unilateral medial rectus (MR) resection and LR recession with the amounts of resection and recession biased to near and distance deviation, respectively, and the A-BLR group with 22 patients who underwent bilateral augmented LR recession based on the near deviation. A successful outcome at distant and near was defined as exodeviation between 10 PD of exophoria/tropia and 5 PD of esophoria/tropia. Cumulative probabilities of success, preoperative and postoperative distant, near deviations, and NDD among groups were analyzed and compared.ResultsThe success rate of distant exodeviation, near exodeviation, and NDD in the three groups after 1 year was statistically insignificant (P=0.054, 0.233, and 0.142, respectively). At the 1 year follow-up, vertical pattern strabismus (V and A patterns) was a feature of the S-BLR group, whereas the rate of postoperative overcorrection and undercorrection was significant in the A-BLR and I-RR groups, respectively.ConclusionThe success rate of correction of distant exodeviation, near exodeviation, and NDD was statistically indifferent among the three groups. However, each procedure has its specific postoperative concerns, which should be considered before implementing in patients with CI-X(T).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Burian HM. Exodeviations: their classification, diagnosis and treatment. Am J Ophthalmol 1966; 62: 1161–1166. - PubMed
-
- Wang B, Wang L, Wang Q, Ren M. Comparison of different surgery procedures for convergence insufficiency-type intermittent in children. Br J Ophthalmol 2014; 98: 1409–1413. - PubMed
-
- Raab EL, Parks MM. Recession of the lateral recti; effect of preoperative fusion and distance-near relationship. Arch Ophthalmol 1975; 93: 584–586. - PubMed
-
- von Noorden GK. Resection of both medial rectus muscles in organic convergence insufficiency. Am J Ophthalmol 1976; 81: 223–226. - PubMed
-
- Nemet P, Stolovich C. Biased resection of the medial recti: a new surgical approach to convergence insufficiency. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q 1990; 5: 213–216.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

