Microsurgical resection of brain arteriovenous malformations in the elderly: outcomes analysis and risk stratification
- PMID: 29271715
- PMCID: PMC6816804
- DOI: 10.3171/2017.6.JNS17392
Microsurgical resection of brain arteriovenous malformations in the elderly: outcomes analysis and risk stratification
Abstract
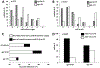
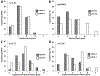
As the population ages, the question of how to manage brain arteriovenous malformations in the elderly becomes increasingly relevant. Is resection a reasonable option for these patients? In this study, the authors examined the outcomes of surgical patients 60 years or older and found that favorable outcomes were achieved with careful patient selection. Preoperative grading scales were more predictive of outcomes in patients older than 65 years than in those 60-65 years of age.
Keywords: AVM = arteriovenous malformation; LFU = last follow-up; Lawton-Young grading system; SM = Spetzler-Martin; Spetzler-Martin grading system; arteriovenous malformation; elderly; mRS = modified Rankin Scale; microsurgical resection; supplemented Spetzler-Martin grading; vascular disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Abecassis IJ, Xu DS, Batjer HH, Bendok BR: Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review. Neurosurg Focus 37(3):E7, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Friedlander RM: Clinical practice. Arteriovenous malformations of the brain. N Engl J Med 356:2704–2712, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto H, Iida J, Kawaguchi S, Sakaki T: Clinical features and management of brain arteriovenous malformations in elderly patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:1091–1098, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Heros RC, Tu YK: Is surgical therapy needed for unruptured arteriovenous malformations? Neurology 37:279–286, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

