On-line hemodiafiltration did not induce an overproduction of oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in intensive care unit-acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29273022
- PMCID: PMC5741969
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0785-1
On-line hemodiafiltration did not induce an overproduction of oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in intensive care unit-acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Though on-line intermittent hemodiafiltration (OL-IHDF) is a routine therapy for chronic dialysis patients, it is not yet widespread used in critically ill patients. This study was undergone to evaluate efficiency and tolerance of OL-IHDF and to appreciate inflammatory consequences of its use in intensive care unit (ICU)-acute kidney injury (AKI) patients.
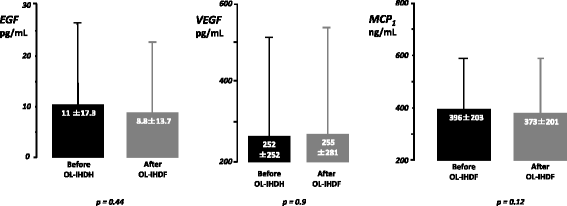
Methods: In this prospective cohort study conducted in a medical academic ICU in France, 30 AKI patients who underwent OL-IHDF were included. OL-HDF used an ultrapure water production: AQ 1250 line with double reverse osmosis, a generator 5008 with a 1.8m2 dialyzer with Polysulfone membrane (Fresenius Medical Care). Tolerance and efficiency of OL-IHDF were evaluated as well as its inflammatory risk by the measurement of plasma concentrations of proinflammatory (Interleukin 6, IL1β, IL8, Interferon γ) and anti-inflammatory (IL4, IL10) cytokines, Epidermal growth factor (EGF), Vascular Endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Macrophage Chemoattractive Protein-1 (MCP-1) before and after sessions.
Results: Intradialytic hypotensive events were observed during 27/203 OL-IHDF sessions accounting for a mal-tolerated session's rate at 13.3%. Mean delivered urea Kt/V per session was 1.12 ± 0.27 with a percentage of reduction for urea, creatinine, β2-microglobulin and cystatine C at 61.6 ± 8.8%, 55.3 ± 6.7%, 51.5 ± 8.7% and 44.5 ± 9.8% respectively. Production of superoxide anion by leukocytes, mean levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and plasmatic concentrations of EGF, VEGF and MCP-1 did not differ before and after OL-IHDF sessions. We observed however a significant decrease of mean TNFα plasmatic concentrations from 8.2 ± 5.8 to 4.8 ± 3.5 pg/ml at the end of OL-IHDF.
Conclusions: OL-IHDF was not associated with an increase in pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress or EGF, VEGF and MCP-1 in AKI patients and seems therefore a secure and feasible modality in ICUs.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Anti-inflammatory cytokines; Egf; Inflammatory cytokines; Mcp-1; On-line Hemodiafiltration; Oxidative stress; Vegf.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This observational prospective study was carried out at the Medical ICU of Lapeyronie University Hospital at Montpellier and was approved by the Ethics Research Committee of our hospital; PHRC régional: N° 2006-A00510–51. A written informed consent was obtained from the patients. If the patient has not the capability to give consent, a written informed consent was obtained from its closest relative. All the patients confirmed their consent by writing later on.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors’ declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Vinsonneau C, Camus C, Combes A, Costa de Beauregard MA, Klouche K, Boulain T, et al. Continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration versus intermittent haemodialysis for acute renal failure in patients with multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2006;368:379–385. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69111-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

