Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and senescence through activating the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 29273676
- PMCID: PMC5897744
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171454
Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and senescence through activating the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and senescence through activating the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway.Biosci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;44(8):BSR-2017-1454_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2017-1454_RET. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39171816 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is closely correlated with disc degeneration. Nucleus pulposus (NP) cell apoptosis and senescence are typical cellular features within the degenerative disc. Resveratrol is a newly identified phytoalexin that has protective effects on cartilaginous tissue.
Objective: To investigate the whether resveratrol can protect against high glucose-induced NP cell apoptosis and senescence, and the potential mechanism in this process.
Methods: Rat NP cells were cultured in either 10% FBS culture medium (control group) or 10% FBS with a high glucose concentration (0.2 M, experiment group) for 3 days. Resveratrol or the combination of resveratrol and LY294002 was added into the culture medium of experiment group to investigate the effects of resveratrol and the PI3K/Akt pathway.
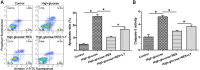
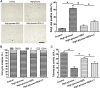
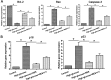
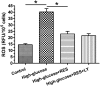
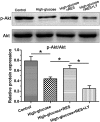
Results: High glucose significantly promoted NP cell apoptosis and NP cell senescence compared with the control group. Resveratrol exhibited protective effects against high glucose-induced NP cell apoptosis and senescence. Further analysis showed that resveratrol suppressed reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and increased the activity of the PI3K/Akt pathway under the high glucose condition. However, the LY294002 had no significant effects on ROS content in the resveratrol-treated high glucose group.
Conclusion: Resveratrol can attenuate high glucose-induced NP cell apoptosis and senescence, and the activation of ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway may be the potential mechanism in this process.
Keywords: apoptosis; glucose; intervertebral disc degeneration; nucleus pulposus; resveratrol; senescence.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

