TNFα blockade overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 in experimental melanoma
- PMID: 29273790
- PMCID: PMC5741628
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02358-7
TNFα blockade overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 in experimental melanoma
Abstract
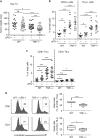
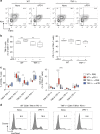
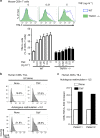
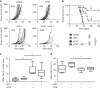
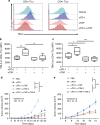
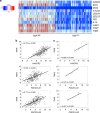
Antibodies against programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) have considerably changed the treatment for melanoma. However, many patients do not display therapeutic response or eventually relapse. Moreover, patients treated with anti-PD-1 develop immune-related adverse events that can be cured with anti-tumor necrosis factor α (TNF) antibodies. Whether anti-TNF antibodies affect the anti-cancer immune response remains unknown. Our recent work has highlighted that TNFR1-dependent TNF signalling impairs the accumulation of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (CD8+ TILs) in mouse melanoma. Herein, our results indicate that TNF or TNFR1 blockade synergizes with anti-PD-1 on anti-cancer immune responses towards solid cancers. Mechanistically, TNF blockade prevents anti-PD-1-induced TIL cell death as well as PD-L1 and TIM-3 expression. TNF expression positively correlates with expression of PD-L1 and TIM-3 in human melanoma specimens. This study provides a strong rationale to develop a combination therapy based on the use of anti-PD-1 and anti-TNF in cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Nicolas Meyer has worked as an investigator and/or consultant and/or speaker for: BMS, MSD, Amgen, Roche, GSK, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. The rest of the authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ratner A, Clark WR. Role of TNF-alpha in CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated lysis. J. Immunol. 1993;150:4303–4314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

