Oral findings in Williams-Beuren syndrome
- PMID: 29274148
- PMCID: PMC5822531
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21834
Oral findings in Williams-Beuren syndrome
Abstract
Background: Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS; OMIM #194050) is a developmental disorder characterized by congenital heart disease, intellectual disability, dysmorphic facial features and ophthalmologic abnormalities. Oral abnormalities are also described in clinical manifestations of the disease. This paper describes orofacial features in patients with WBS.
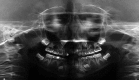
Material and methods: Seventeen patients with a confirmed molecular diagnosis of WBS were examined for oral abnormalities through clinical oral evaluations and panoramic radiography.
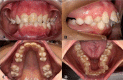
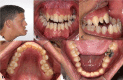
Results: Malocclusion, specifically with dental midline deviation, and high-arched palate were the most common findings.
Conclusions: The present results contribute to knowledge on the orofacial manifestations of WBS. Since such patients with WBS may develop severe oral abnormalities, early detection and treatment can help improve their quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
OROFACIAL FINDINGS AND DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF WILLIAMS SYNDROME.Genet Couns. 2015;26(4):437-42. Genet Couns. 2015. PMID: 26852515
-
Orthodontic orthognathic surgical treatment of a subject with Williams Beuren syndrome a follow-up from 8 to 25 years of age.Eur J Orthod. 2007 Aug;29(4):332-7. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjm031. Eur J Orthod. 2007. PMID: 17702793
-
Lower urinary tract symptoms in children and adolescents with Williams-Beuren syndrome.J Pediatr Urol. 2017 Apr;13(2):203.e1-203.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Nov 2. J Pediatr Urol. 2017. PMID: 27876405
-
Severe left main coronary artery stenosis with abnormal branching pattern in a patient with mild supravalvar aortic stenosis and Williams-Beuren syndrome.Congenit Heart Dis. 2014 May-Jun;9(3):E85-9. doi: 10.1111/chd.12087. Epub 2013 May 22. Congenit Heart Dis. 2014. PMID: 23701710 Review.
-
Diagnosis and management of medical problems in adults with Williams-Beuren syndrome.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2007 Aug 15;145C(3):280-90. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30139. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17639596 Review.
Cited by
-
Knowledge and attitudes about rare genetic diseases among practitioners of oral medicine/pathology in Brazil: a cross-sectional study.Front Oral Health. 2025 Jul 7;6:1573355. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1573355. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40692699 Free PMC article.
-
RFC2 may contribute to the pathogenicity of Williams syndrome revealed in a zebrafish model.J Genet Genomics. 2024 Dec;51(12):1389-1403. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2024.09.016. Epub 2024 Oct 4. J Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39368701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baltimore: 2016. [ cited 12 Dic 2016 ]. On-line Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM (TM) Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. MIM Number: 194050. [Internet] Available from: http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/
-
- Strøme P, Bjornstad P, Ramstad K. Prevalence estimation of Williams syndrome. J Child Neurol. 2002;17:269–271. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics (Committee on Genetics. Health Care Supervision for Children with Williams Syndrome. Pediatrics. 2001;107:1192–1204. - PubMed
-
- Morris CA, Loker J, Ensing G, Stock AD. Supravalvular aortic stenosis cosegregates with a familial 6:7 translocation which disrupts the elastin gene. Am J Med Genet. 1993;46:737–744. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

