Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 attenuates house dust mite-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation by suppressing dendritic cell-mediated adaptive immune responses
- PMID: 29274414
- PMCID: PMC6013321
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.10.044
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 attenuates house dust mite-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation by suppressing dendritic cell-mediated adaptive immune responses
Abstract
Background: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP-1) is a scavenger receptor that regulates adaptive immunity and inflammation. LRP-1 is not known to modulate the pathogenesis of allergic asthma.
Objective: We sought to assess whether LRP-1 expression by dendritic cells (DCs) modulates adaptive immune responses in patients with house dust mite (HDM)-induced airways disease.
Methods: LRP-1 expression on peripheral blood DCs was quantified by using flow cytometry. The role of LRP-1 in modulating HDM-induced airways disease was assessed in mice with deletion of LRP-1 in CD11c+ cells (Lrp1fl/fl; CD11c-Cre) and by adoptive transfer of HDM-pulsed CD11b+ DCs from Lrp1fl/fl; CD11c-Cre mice to wild-type (WT) mice.
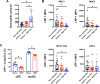
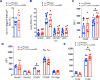
Results: Human peripheral blood myeloid DC subsets from patients with eosinophilic asthma have lower LRP-1 expression than cells from healthy nonasthmatic subjects. Similarly, LRP-1 expression by CD11b+ lung DCs was significantly reduced in HDM-challenged WT mice. HDM-challenged Lrp1fl/fl; CD11c-Cre mice have a phenotype of increased eosinophilic airway inflammation, allergic sensitization, TH2 cytokine production, and mucous cell metaplasia. The adoptive transfer of HDM-pulsed LRP-1-deficient CD11b+ DCs into WT mice generated a similar phenotype of enhanced eosinophilic inflammation and allergic sensitization. Furthermore, CD11b+ DCs in the lungs of Lrp1fl/fl; CD11c-Cre mice have an increased ability to take up HDM antigen, whereas bone marrow-derived DCs display enhanced antigen presentation capabilities.
Conclusion: This identifies a novel role for LRP-1 as a negative regulator of DC-mediated adaptive immune responses in the setting of HDM-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation. Furthermore, the reduced LRP-1 expression by circulating myeloid DCs in patients with eosinophilic asthma suggests a possible role for LRP-1 in modulating type 2-high asthma.
Keywords: Low-density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 1; dendritic cells; eosinophilic airway inflammation; house dust mite; type 2–high asthma.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Krieger M, Herz J. Structures and functions of multiligand lipoprotein receptors: macrophage scavenger receptors and LDL receptor-related protein (Lrp) Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1994;63:601–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

