Prostaglandin E2 as a Regulator of Immunity to Pathogens
- PMID: 29274705
- PMCID: PMC5898978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.12.008
Prostaglandin E2 as a Regulator of Immunity to Pathogens
Abstract
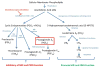
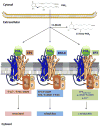
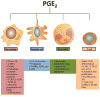
The body is exposed to foreign pathogens every day, but remarkably, most pathogens are effectively cleared by the innate immune system without the need to invoke the adaptive immune response. Key cellular components of the innate immune system include macrophages and neutrophils and the recruitment and function of these cells are tightly regulated by chemokines and cytokines in the tissue space. Innate immune responses are also known to regulate development of adaptive immune responses often via the secretion of various cytokines. In addition to these protein regulators, numerous lipid mediators can also influence innate and adaptive immune functions. In this review, we cover one particular lipid regulator, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and describe its synthesis and signaling and what is known about the ability of this lipid to regulate immunity and host defense against viral, fungal and bacterial pathogens.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; eicosanoids; host defense; inflammation; innate immunity; pathogen.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ahn KB, Jeon JH, Baik JE, Park OJ, Kang SS, Yun CH, Park JH, Han SH. Muramyl dipeptide potentiates staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Microbes Infect. 2014;16:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Akaogi J, Yamada H, Kuroda Y, Nacionales DC, Reeves WH, Satoh M. Prostaglandin E2 receptors EP2 and EP4 are up-regulated in peritoneal macrophages and joints of pristane-treated mice and modulate TNF-alpha and IL-6 production. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:227–236. Epub 2004 Apr 2001. - PubMed
-
- Allie SR, Randall TD. Pulmonary immunity to viruses. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017;131:1737–1762. - PubMed
-
- Almeida PE, Roque NR, Magalhaes KG, Mattos KA, Teixeira L, Maya-Monteiro C, Almeida CJ, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Ryffel B, Quesniaux VF, Bozza PT. Differential TLR2 downstream signaling regulates lipid metabolism and cytokine production triggered by Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1841:97–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

