The Multifaceted Role of the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex in Emotion, Decision Making, Social Cognition, and Psychopathology
- PMID: 29275839
- PMCID: PMC5862740
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.10.030
The Multifaceted Role of the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex in Emotion, Decision Making, Social Cognition, and Psychopathology
Abstract
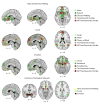
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) has been implicated in a variety of social, cognitive, and affective functions that are commonly disrupted in mental illness. In this review, we summarize data from a diverse array of human and animal studies demonstrating that the vmPFC is a key node of cortical and subcortical networks that subserve at least three broad domains of psychological function linked to psychopathology. One track of research indicates that the vmPFC is critical for the representation of reward- and value-based decision making, through interactions with the ventral striatum and amygdala. A second track of research demonstrates that the vmPFC is critical for the generation and regulation of negative emotion, through its interactions with the amygdala, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, periaqueductal gray, hippocampus, and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex. A third track of research shows the importance of the vmPFC in multiple aspects of social cognition, such as facial emotion recognition, theory-of-mind ability, and processing self-relevant information, through its interactions with the posterior cingulate cortex, precuneus, dorsomedial PFC, and amygdala. We then present meta-analytic data revealing distinct subregions within the vmPFC that correspond to each of these three functions, as well as the associations between these subregions and specific psychiatric disorders (depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, addiction, social anxiety disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder). We conclude by describing several translational possibilities for clinical studies of vmPFC-based circuits, including neuropsychological assessment of transdiagnostic functions, anatomical targets for intervention, predictors of treatment response, markers of treatment efficacy, and subtyping within disorders.
Keywords: Decision making; Emotion; Neuroanatomy; Prefrontal cortex; Psychopathology; Social cognition.
Copyright © 2017 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mackey S, Petrides M. Architecture and morphology of the human ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Eur J Neurosci. 2014;40:2777–2796. - PubMed
-
- Ongur D, Ferry AT, Price JL. Architectonic subdivision of the human orbital and medial prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol. 2003;460:425–449. - PubMed
-
- Ongur D, Price JL. The organization of networks within the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex of rats, monkeys and humans. Cereb Cortex. 2000;10:206–219. - PubMed
-
- Eslinger PJ, Damasio AR. Severe disturbance of higher cognition after bilateral frontal lobe ablation: patient EVR. Neurology. 1985;35:1731–1741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

