Molecular Mechanisms for CFIm-Mediated Regulation of mRNA Alternative Polyadenylation
- PMID: 29276085
- PMCID: PMC5756121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.031
Molecular Mechanisms for CFIm-Mediated Regulation of mRNA Alternative Polyadenylation
Abstract
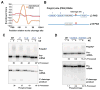
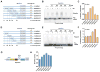
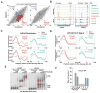
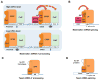
Alternative mRNA processing is a critical mechanism for proteome expansion and gene regulation in higher eukaryotes. The SR family proteins play important roles in splicing regulation. Intriguingly, mammalian genomes encode many poorly characterized SR-like proteins, including subunits of the mRNA 3'-processing factor CFIm, CFIm68 and CFIm59. Here we demonstrate that CFIm functions as an enhancer-dependent activator of mRNA 3' processing. CFIm regulates global alternative polyadenylation (APA) by specifically binding and activating enhancer-containing poly(A) sites (PASs). Importantly, the CFIm activator functions are mediated by the arginine-serine repeat (RS) domains of CFIm68/59, which bind specifically to an RS-like region in the CPSF subunit Fip1, and this interaction is inhibited by CFIm68/59 hyper-phosphorylation. The remarkable functional similarities between CFIm and SR proteins suggest that interactions between RS-like domains in regulatory and core factors may provide a common activation mechanism for mRNA 3' processing, splicing, and potentially other steps in RNA metabolism.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; SR proteins; alternative polyadenylation; cleavage; mRNA 3′ processing; polyadenylation; splicing.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Baron-Benhamou J, Gehring NH, Kulozik AE, Hentze MW. Using the lambdaN peptide to tether proteins to RNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;257:135–154. - PubMed
-
- Brown KM, Gilmartin GM. A mechanism for the regulation of pre-mRNA 3′ processing by human cleavage factor Im. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1467–1476. - PubMed
-
- Cao W, Garcia-Blanco MA. A serine/arginine-rich domain in the human U1 70k protein is necessary and sufficient for ASF/SF2 binding. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:20629–20635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

