Cost-effectiveness analysis of IDegLira versus basal-bolus insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes in the Slovak health system
- PMID: 29276398
- PMCID: PMC5731336
- DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S143127
Cost-effectiveness analysis of IDegLira versus basal-bolus insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes in the Slovak health system
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the cost-effectiveness of once-daily insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) versus basal-bolus therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes not meeting glycemic targets on basal insulin from a healthcare payer perspective in Slovakia.
Methods: Long-term clinical and economic outcomes for patients receiving IDegLira and basal-bolus therapy were estimated using the IMS CORE Diabetes Model based on a published pooled analysis of patient-level data.
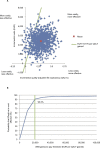
Results: IDegLira was associated with an improvement in quality-adjusted life expectancy of 0.29 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) compared with basal-bolus therapy. The average lifetime cost per patient in the IDegLira arm was EUR 2,449 higher than in the basal-bolus therapy arm. Increased treatment costs with IDegLira were partially offset by cost savings from avoided diabetes-related complications. IDegLira was highly cost-effective versus basal-bolus therapy with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of EUR 8,590 per QALY gained, which is well below the cost-effectiveness threshold set by the law in Slovakia.
Conclusion: IDegLira is cost-effective in Slovakia, providing a simple option for intensification of basal insulin therapy without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia or weight gain and with fewer daily injections than a basal-bolus regimen.
Keywords: IDegLira; basal-bolus; cost-effective; insulin intensification; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure N Racekova, A Ramirez de Arellano, and T Vandebrouck are employees of Novo Nordisk. B Hunt is an employee of Ossian Health Economics and Communications. Ossian received consulting fees from Novo Nordisk to support the analysis. M Bucek Psenkova is the general manager of Pharm-In and M Psota is an employee of Pharm-In. Pharm-In received consulting fees from Novo Nordisk to support the analysis. The authors acknowledge the assistance of DRG Abacus (sponsored by Novo Nordisk) for medical writing and editorial support. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tobacco report. Geneva: World Health Organization; [Accessed October 5, 2017]. Available from: http://www.who.int/tobacco/media/en/Slovakia.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization . Global alcohol report. Geneva: World Health Organization; [Accessed October 5, 2017]. Available from: http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/global_alcohol_report/pr....
-
- Buse JB, Vilsbøll T, Thurman J, et al. NN9068-3912 (DUAL-II) Trial Investigators Contribution of liraglutide in the fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) Diabetes Care. 2014;37(11):2926–2933. - PubMed
-
- Psota M, Ondrušová M, Pšenková M, Martinka E, Ilavská A. Využívanie zdravotnej starostlivosti a nákladovosť liečby diabetu a jeho komplikácií pre potreby hodnotenia nákladovej efektívnosti zdravotníckych intervencií pomocou modelu CORE na Slovensku [Health Care Resource Use and Cost of Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications for Assessing the Cost Effectiveness of Medical Interventions using the CORE Model in Slovakia] Bratislava: Pharm-In; 2015. Slovak.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

