Rapidly Growing Thalamic Abscess
- PMID: 29276565
- PMCID: PMC5734503
- DOI: 10.1177/1941874417700773
Rapidly Growing Thalamic Abscess
Keywords: Streptococcus intermedius (Milleri); brain abscess; cerebral infection; thalamic abscess; thalamic lesion.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
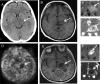
References
-
- Kothari RU, Brott T, Broderick JP, et al. The ABCs of measuring intracerebral hemorrhage volumes. Stroke. 1996;27:1304–1305. - PubMed
-
- Kang K, Lim I, Roh JK. Positron emission tomographic findings in a tuberculosis brain abscess. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21(5):303–306. - PubMed
-
- Mishra AK, Fournier PE. The role of Streptococcus intermedius in brain abscess. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;32(4):477–483. - PubMed
-
- Heckmann JG, Pauli S. Epidural abscess after dental extraction. Age Ageing. 2015;44(5):901. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
