Abnormal expression of TFIIIB subunits and RNA Pol III genes is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29276645
- PMCID: PMC5739085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.08.005
Abnormal expression of TFIIIB subunits and RNA Pol III genes is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
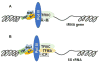
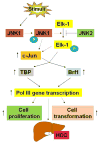
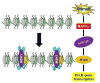
The levels of the products of RNA polymerase III-dependent genes (Pol III genes), including tRNAs and 5S rRNA, are elevated in transformed and tumor cells, which potentiate tumorigenesis. TFIIB-related factor 1 (Brf1) is a key transcription factor and specifically regulates the transcription of Pol III genes. In vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that a decrease in Brf1 reduces Pol III gene transcription and is sufficient for inhibiting cell transformation and tumor formation. Emerging evidence indicates that dysregulation of Brf1 and Pol III genes is linked to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in humans and animals. We have reported that Brf1 is overexpressed in human liver cancer patients and that those with high Brf1 levels have shorter survivals. This review summarizes the effects of dysregulation of these genes on HCC and their regulation by signaling pathways and epigenetics. These novel data should help us determine the molecular mechanisms of HCC from a different perspective and guide the development of therapeutic approaches for HCC patients.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Histone H3; RNA polymerase III; TFIIB-related factor 1 (Brf1); c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNKs).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alcohol Intake and Abnormal Expression of Brf1 in Breast Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 31;2019:4818106. doi: 10.1155/2019/4818106. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of phosphorylated histone H3 serine 10 in DEN-induced deregulation of Pol III genes and cell proliferation and transformation.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2460-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt219. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23774401 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen- and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase 1 Mediates Alcohol-Upregulated Transcription of Brf1 and tRNA Genes to Cause Phenotypic Alteration.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 27;2020:2067959. doi: 10.1155/2020/2067959. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32685086 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of histone H3 serine 28 modulates RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription.Oncogene. 2011 Sep 15;30(37):3943-52. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.105. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21460852 Free PMC article.
-
ROS Signaling-Mediated Novel Biological Targets: Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 4;2021:5888432. doi: 10.1155/2021/5888432. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9890237. doi: 10.1155/2024/9890237. PMID: 34646425 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol Intake and Abnormal Expression of Brf1 in Breast Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 31;2019:4818106. doi: 10.1155/2019/4818106. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of BRF2 inhibits the growth and metastasis of lung cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Sep;22(3):1767-1774. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11285. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32705258 Free PMC article.
-
Role of betaine in inhibiting the induction of RNA Pol III gene transcription and cell growth caused by alcohol.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Jul 1;325:109129. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109129. Epub 2020 May 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32418914 Free PMC article.
-
Early Growth Response 1 Strengthens Pol-III-Directed Transcription and Transformed Cell Proliferation by Controlling PTEN/AKT Signalling Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4930. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094930. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563324 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures of human RNA polymerase III in its unbound and transcribing states.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;28(2):210-219. doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-00555-5. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33558764 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
