Subtilisin inhibitor like protein ' pp LPI-1' from leaves of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan, cv. BSMR 736) exhibits inhibition against Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases
- PMID: 29276657
- PMCID: PMC5726997
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-017-1040-y
Subtilisin inhibitor like protein ' pp LPI-1' from leaves of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan, cv. BSMR 736) exhibits inhibition against Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases
Abstract
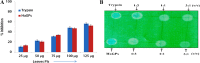
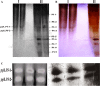
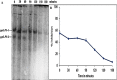
Helicoverpa armigera is an orthodox rival of many crop plants affecting agricultural economy. Plant leaves found to accumulate proteinase inhibitors, although this insect pest chooses leaves for laying eggs. Plant defense response at this juncture is not fully explored. In this context, here we are reporting proteinase inhibitor (ppLPI-1) having significant homology with the I13 family from leaves of pigeonpea (cv. BSMR 736). The isolation of ppLPI-1 was carried out from leaves of field-grown pigeonpea under an outbreak of H. armigera. The acetone precipitated ppLPI-1 (125 µg) displayed substantial inhibition potential towards bovine trypsin (56.5 ± 1.8%) and HaGPs (52.6 ± 1.7%) on solution assay. These results were corroborated with dot-blot analysis. The molecular form of ppLPI-1 was characterized by reverse zymography and GXCP. The optimum condition was found to be pH 8 and temperature in the range of 30-40 °C. The protein identification via MASCOT-PMF and NCBI-BLAST search showed substantial homology with an inducible subtilisin inhibitor of Fabaceae comprising Vigna angularis (96%), Canavalia lineata (78%), Cicer arietinum (76%), Glycine max (75%), Medicago truncatula (73%) and Vicia faba (73%) consists of conserved domain of potato inhibitor I family.
Keywords: HaGPs; Helicoverpa armigera; Pigeonpea; Proteinase inhibitor; Subtilisin inhibitor; ppLPI-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declares that there is no conflict of intrest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Kunitz trypsin inhibitor from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) that exerts anti-metabolic effect on podborer (Helicoverpa armigera) larvae.Plant Mol Biol. 2005 Feb;57(3):359-74. doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-7925-2. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15830127
-
Differential inhibition of Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases by proteinase inhibitors of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) and its wild relatives.Phytochemistry. 2003 Oct;64(3):681-7. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(03)00375-3. Phytochemistry. 2003. PMID: 13679090
-
In vivo inhibition of Helicoverpa armigera gut pro-proteinase activation by non-host plant protease inhibitors.J Insect Physiol. 2010 Sep;56(9):1315-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 28. J Insect Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20416317
-
Successive use of non-host plant proteinase inhibitors required for effective inhibition of helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases and larval growth.Plant Physiol. 1999 Oct;121(2):497-506. doi: 10.1104/pp.121.2.497. Plant Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10517841 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Partial Characterization of Trypsin-Specific Proteinase Inhibitors from Pigeonpea Wild Relative Cajanus platycarpus L. (Fabaceae) Active against Gut Proteases of Lepidopteran Pest Helicoverpa armigera.Front Physiol. 2016 Sep 7;7:388. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00388. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27656149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Thummaratwasik P. Isolation and characterization of trypsin inhibitors from some thai legume seeds. J Food Biochem. 2000;24:107–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4514.2000.tb00689.x. - DOI
-
- Broadway RM, Duffey SS. Plant proteinase inhibitors: mechanism of action and effect on the growth and digestive physiology of larval Heliothis zea and Spodoptera exigua. J Insect Physiol. 1986;32:827–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(86)90097-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

