Upregulation of miR-221 and -222 in response to increased extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 activity exacerbates neointimal hyperplasia in diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 29276985
- PMCID: PMC5812823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.12.016
Upregulation of miR-221 and -222 in response to increased extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 activity exacerbates neointimal hyperplasia in diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background and aims: Diabetes is associated with accelerated arterial intimal thickening that contributes to the increased cardiovascular disease seen in this population. In healthy arteries, intimal thickening is inhibited by elevated levels of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p27Kip1, and intimal thickening is promoted by activation of the mammalian Target of Rapamycin to promote degradation of p27Kip1 protein. Recently, we reported that two microRNAs, miR-221 and -222, which promote intimal thickening via down-regulation of mRNA encoding p27Kip1, are elevated in the arteries of diabetic patients. To determine if these miRNAs are critical to the increased intimal thickening under diabetic conditions, we examined the regulation of p27Kip1in a mouse model of diabetes.
Methods: Comparisons of p27Kip1 signaling in NONcNZO10 mice fed a diabetogenic versus control diet were performed using immunochemistry and real-time PCR.
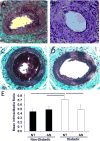
Results: Vascular smooth muscle cells and arteries of diabetic mice exhibited decreased levels of p27Kip1 that derived from destabilization of p27Kip1 mRNA in an extracellular signal response kinase-1/2 (ERK-1/2) dependent manner. The activity of ERK-1/2 is increased in the arteries of diabetic mice and promotes an increase in miR-221 and -222. Inhibition of miR-221 and -222 restores normal levels of p27Kip1 mRNA and protein in the arteries of diabetic mice and reduces intimal thickening following wire injury.
Conclusions: These data suggest diabetes is accompanied by increases in arterial miR-221 and -222 expression that promotes intimal thickening. Inhibition of the increased miR-221 and -222 may be efficacious in the prevention of the cardiovascular complications of diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Intimal thickening; miR-221; miR-222; p27(Kip1).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared they do not have anything to disclose regarding conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Figures
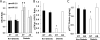



References
-
- Faries PL, Rohan DI, Takahara H, et al. Human vascular smooth muscle cells of diabetic origin exhibit increased proliferation, adhesion, and migration. J Vasc Surg. 2001;33:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Kornowski R, Mintz GS, Kent KM, et al. Increased restenosis in diabetes mellitus after coronary interventions is due to exaggerated intimal hyperplasia. A serial intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation. 1997;95:1366–1369. - PubMed
-
- Niskanen L, Rauramaa R, Miettinen H, et al. Carotid artery intima-media thickness in elderly patients with NIDDM and in nondiabetic subjects. Stroke. 1996;27:1986–1992. - PubMed
-
- Yamasaki Y, Kawamori R, Matsushima H, et al. Asymptomatic hyperglycaemia is associated with increased intimal plus medial thickness of the carotid artery. Diabetologia. 1995;38:585–591. - PubMed
-
- Chung J, Kuo CJ, Crabtree GR, et al. Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signaling by the 70 kd S6 protein kinases. Cell. 1992;69:1227–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

