Diaphragm: Pathophysiology and Ultrasound Imaging in Neuromuscular Disorders
- PMID: 29278898
- PMCID: PMC5836400
- DOI: 10.3233/JND-170276
Diaphragm: Pathophysiology and Ultrasound Imaging in Neuromuscular Disorders
Abstract
Respiratory muscles are classically involved in neuromuscular disorders, leading to a restrictive respiratory pattern. The diaphragm is the main respiratory muscle involved during inspiration. Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive, radiation-free, accurate and safe technique allowing assessment of diaphragm anatomy and function. The authors review the pathophysiology of diaphragm in neuromuscular disorders, the methodology and indications of diaphragm ultrasound imaging as well as possible pitfalls in the interpretation of results.
Keywords: Diaphragm; neuromuscular disorders; ultrasound.
Figures
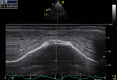
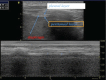
References
-
- Mead J, Loring SH. Analysis of volume displacement and length changes of the diaphragm during breathing. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982;53(3):750–5. - PubMed
-
- Bushby K, Finkel R, Birnkrant DJ, Case LE, Clemens PR, Cripe L, Kaul A, Kinnett K, McDonald C, Pandya S, Poysky J, Shapiro F, Tomezsko J, Constantin C, DMD Care Considerations Working Group. Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 2: Implementation of multidisciplinary care. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(2):177–89. - PubMed
-
- Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Cohen RA, Langer JC. Multimodality imaging of the pediatric diaphragm: Anatomy and pathologic conditions. Radiographics. 2010;30(7):1797–817. - PubMed
-
- McCool FD, Tzelepis GE. Dysfunction of the diaphragm. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(10):932–42. - PubMed
-
- Wait JL, Nahormek PA, Yost WT, Rochester DP. Diaphragmatic thickness-lung volume relationship in vivo. J Appl Physiol. 1989;67(4):1560–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

