Role of vitamin D deficiency in systemic lupus erythematosus incidence and aggravation
- PMID: 29280010
- PMCID: PMC5743852
- DOI: 10.1007/s13317-017-0101-x
Role of vitamin D deficiency in systemic lupus erythematosus incidence and aggravation
Abstract
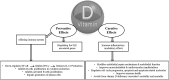
Vitamin D is one of the main groups of sterols; playing an important role in phospho-calcic metabolism. The conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to pre- vitamin D3 in the skin, through solar ultraviolet B radiation, is the main source of vitamin D. Since lupus patients are usually photosensitive, the risk of developing vitamin D deficiency in is high in this population. Although evidences showed the connotation between systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and vitamin D through which SLE can lead to lower vitamin D levels, it is also important to consider the possibility that vitamin D deficiency may have a causative role in SLE etiology. This paper analyzes existing data from various studies to highlight the role of vitamin D deficiency in SLE occurrence and aggravation and the probable efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on SLE patients. We searched "Science Direct" and "Pub Med" using "Vitamin D" and "SLE" for finding the studies focusing on the association between vitamin D deficiency and SLE incidence and consequences. Evidences show that vitamin D plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of SLE and vitamin D supplementation seems to ameliorate inflammatory and hemostatic markers; so, can improve clinical subsequent.
Keywords: SLE aggravation; SLE incidence; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Vitamin D deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
There is no informed consent required for this manuscript.
Human and animal rights
There are no human or animal rights to be considered in this manuscript.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical