Macitentan in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Focus on Combination Therapy in the SERAPHIN Trial
- PMID: 29280064
- PMCID: PMC5772137
- DOI: 10.1007/s40256-017-0260-1
Macitentan in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Focus on Combination Therapy in the SERAPHIN Trial
Abstract
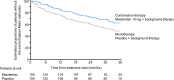
SERAPHIN was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, event-driven phase III trial that evaluated the effects of long-term treatment with macitentan, an oral endothelin receptor antagonist, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The majority of patients were receiving PAH therapy at enrollment, providing the opportunity to evaluate the efficacy and safety of macitentan in combination with other PAH therapies (predominantly phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors [PDE-5i]). In patients receiving background therapy, macitentan reduced the risk of morbidity/mortality by 38% compared with placebo (hazard ratio [HR] 0.62; 95% confidence level [CL] 0.43-0.89; p = 0.009). Furthermore, patients receiving macitentan and background therapy had a 37% reduction in the risk of being hospitalized for PAH (HR 0.63; 95% CL 0.41-0.96) compared with patients receiving background therapy only (placebo arm). Macitentan treatment in combination with background therapy was also associated with improvements in exercise capacity, functional class, cardiopulmonary hemodynamics, and health-related quality of life compared with background therapy alone. The safety profile of macitentan as part of a combination therapy regimen was consistent with that of macitentan in the overall SERAPHIN population. The SERAPHIN study has provided evidence that combination therapy with macitentan and a PDE-5i is effective and well tolerated in the management of PAH. Based on these data, and those from subsequent long-term trials, combination therapy is increasingly recognized as an important treatment option for improving long-term outcomes in PAH.
Clinical trial registration number: NCT00660179.
Conflict of interest statement
Pavel Jansa has received fees and grants from Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd, United Therapeutics, AOP Orphan, Bayer HealthCare, MSD, and GlaxoSmithKline. He has served on advisory boards for Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Bayer HealthCare, and MSD. Tomás Pulido’s institution has received research grants from Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd, United Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer HealthCare, and Reata Pharmaceuticals. He has served as a consultant and received honoraria for lectures from Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Bayer HealthCare, and GlaxoSmithKline. He has participated as a principal investigator in trials sponsored by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Focus on Macitentan in the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Aug;123(2):103-113. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13033. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29719121 Review.
-
Development of macitentan for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Nov;1358:68-81. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12856. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26291180 Review.
-
[The new endothelin receptor antagonist macitentan: Prospects for therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension].Ter Arkh. 2016;88(7):89-97. doi: 10.17116/terarkh201688789-97. Ter Arkh. 2016. PMID: 27459621 Review. Russian.
-
Modeling of pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and hemodynamic effects of macitentan in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;49:140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29501590 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-Term Safety, Tolerability and Survival in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Treated with Macitentan: Results from the SERAPHIN Open-Label Extension.Adv Ther. 2022 Sep;39(9):4374-4390. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02199-x. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35819570 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis.Integr Blood Press Control. 2020 Mar 23;13:15-29. doi: 10.2147/IBPC.S232038. eCollection 2020. Integr Blood Press Control. 2020. PMID: 32280271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical use of macitentan in the treatment of connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Mar 29;16(3):2060-2069. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-151. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38617769 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Hypertension Phenotypes in Systemic Sclerosis: The Right Diagnosis for the Right Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;21(12):4430. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124430. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32580360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver injury due to endothelin receptor antagonists: a real-world study based on post-marketing drug monitoring data.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17534666231223606. doi: 10.1177/17534666231223606. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024. PMID: 38179676 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world treatment patterns, healthcare resource utilization, and cost among adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension in the United States.Pulm Circ. 2022 Jun 8;12(2):e12090. doi: 10.1002/pul2.12090. eCollection 2022 Apr. Pulm Circ. 2022. PMID: 35795495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Heart J. 2016;37:67–119. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Respir J. 2015;46:903–975. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01032-2015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

