Suppression of STAT3 NH2 -terminal domain chemosensitizes medulloblastoma cells by activation of protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 via de-repression by microRNA-21
- PMID: 29280516
- PMCID: PMC6132241
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.22778
Suppression of STAT3 NH2 -terminal domain chemosensitizes medulloblastoma cells by activation of protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 via de-repression by microRNA-21
Abstract
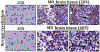
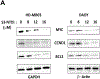
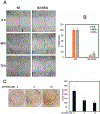
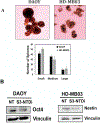
Medulloblastoma (MB) is a malignant pediatric brain tumor with poor prognosis. Signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 (STAT3) is constitutively activated in MB where it functions as an oncoprotein, mediating cancer progression and metastasis. Here, we have delineated the functional role of activated STAT3 in MB, by using a cell permeable STAT3-NH2 terminal domain inhibitor (S3-NTDi) that specifically perturbs the structure/function of STAT3. We have implemented several biochemical experiments using human MB tumor microarray (TMA) and pediatric MB cell lines, derived from high-risk SHH-TP53-mutated and MYC-amplified Non-WNT/SHH tumors. Treatment of MB cells with S3-NTDi leads to growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis. S3-NTDi downregulated expression of STAT3 target genes, delayed migration of MB cells, attenuated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker expressions and reduced cancer stem-cell associated protein expressions in MB-spheres. To elucidate mechanisms, we showed that S3-NTDi induce expression of pro-apoptotic gene, C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP), and decrease association of STAT3 to the proximal promoter of CCND1 and BCL2. Of note, S3-NTDi downregulated microRNA-21, which in turn, de-repressed Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT3 (PIAS3), a negative regulator of STAT3 signaling pathway. Furthermore, combination therapy with S3-NTDi and cisplatin significantly decreased highly aggressive MYC-amplified MB cell growth and induced apoptosis by downregulating STAT3 regulated proliferation and anti-apoptotic gene expression. Together, our results revealed an important role of STAT3 in regulating MB pathogenesis. Disruption of this pathway with S3-NTDi, therefore, may serves as a promising candidate for targeted MB therapy by enhancing chemosensitivity of MB cells and potentially improving outcomes in high-risk patients.
Keywords: MYC; PIAS3; STAT3; medulloblastoma; miR-21.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures










References
-
- Gilbertson RJ, Ellison DW: The origins of medulloblastoma subtypes. Annu Rev Pathol 2008, 3:341–365. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg JF: Activation of STAT proteins and growth control. Bioessays 2001, 23(2):161–169. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE, Jr., Kerr IM, Stark GR: Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264(5164):1415–1421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

