Temporal fluctuations in regional myocardial flows
- PMID: 2928084
- PMCID: PMC3655777
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00584480
Temporal fluctuations in regional myocardial flows
Abstract
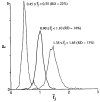
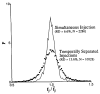
Considerable spatial heterogeneity has been observed in regional myocardial blood flow in isolated hearts and in both anesthetized and conscious animals. In order to study how local blood flow varies with time, the data obtained by King et al. (1985) from ten awake, healthy baboons were analyzed to estimate the role of temporal fluctuations. Four to six distributions of regional flows were estimated at intervals of 4 min to 27 h, using 15 mu diameter microspheres and dividing each heart into 204 locatable pieces (average piece mass = 0.17 g). The technique averages over the 40 s of the injection giving no measure of fluctuations over a few seconds. The temporal variation in regional blood flow, expressed as the relative dispersion (SD/mean) of the temporally separated measurements about the mean flow for each piece and corrected for methodological noise, was 12% for the whole heart (10828 observations). For the left ventricle, the temporal variation was 10% (8806 observations), for the right ventricle 14% (1455 observations), and for the atria 22% (567 observations). On a relative basis, temporal fluctuation was greatest in regions having low flows. Since the magnitude of the changes in flow distributions was the same after 4 min as it was in several hours, we conclude that much of the "twinkling" is a high frequency phenomenon occurring over seconds to a few minutes. Further, it is concluded that regional myocardial blood flow in conscious primates is relatively stable with time, temporal fluctuations causing only about one third of the variation between regions.
Figures



References
-
- Baer RW, Payne BD, Verrier ED, Vlahakes GJ, Molodowitch D, Uhlig PN, Hoffman JIE. Increased number of myocardial blood flow measurements with radionuclide-labeled microspheres. Am J Physiol. 1984;246:H418–H434. - PubMed
-
- Bassingthwaighte JB, Dobbs WA, Yipintsoi T. Heterogeneity of myocardial blood flow. In: Maseri A, editor. Myocardial blood flow in man: methods and significance in coronary disease. Minerva Medica; Torino: 1972. pp. 197–205.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
