Comparison of line probe assay to BACTEC MGIT 960 system for susceptibility testing of first and second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs in a referral laboratory in South Africa
- PMID: 29282012
- PMCID: PMC5745758
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2898-3
Comparison of line probe assay to BACTEC MGIT 960 system for susceptibility testing of first and second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs in a referral laboratory in South Africa
Abstract
Background: The incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is increasing and the emergence of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is a major challenge. Controlling resistance, reducing transmission and improving treatment outcomes in MDR/XDR-TB patients is reliant on susceptibility testing. Susceptibility testing using phenotypic methods is labour intensive and time-consuming. Alternative methods, such as molecular assays are easier to perform and have a rapid turn-around time. The World Health Organization (WHO) has endorsed the use of line probe assays (LPAs) for first and second line diagnostic screening of MDR/XDR-TB.
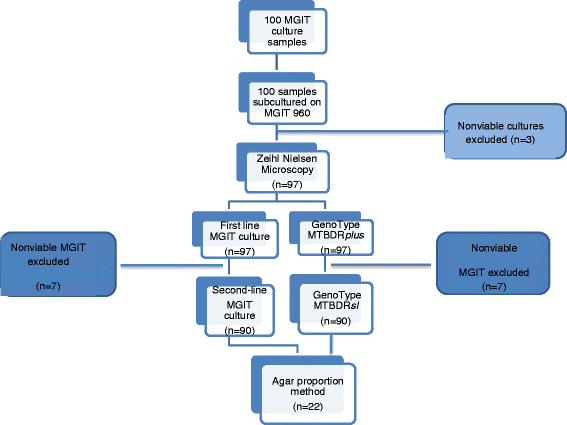
Methods: We compared the performance of LPAs to BACTEC MGIT 960 system for susceptibility testing of bacterial resistance to first-line drugs: rifampicin (RIF), isoniazid (INH), ethambutol (EMB), and second-line drugs ofloxacin (OFL) and kanamycin (KAN). One hundred (100) consecutive non-repeat Mycobacterium tuberculosis cultures, resistant to either INH or RIF or both, as identified by BACTEC MGIT 960 were tested. All isoniazid resistant cultures (n = 97) and RIF resistant cultures (n = 90) were processed with Genotype®MTBDRplus and Genotype®MTBDRsl line probe assays (LPAs). The agar proportion method was employed to further analyze discordant LPAs and the MGIT 960 isolates.
Results: The Genotype ®MTBDRplus (version 2) sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV from culture isolates were as follows: RIF, 100%, 87.9, 58.3% and 100%; INH, 100%, 94.4%, 93.5% and 100%. The sensitivity, specificity PPV and NPV for Genotype ® MTBDRsl (version 1 and 2) from culture isolates were as follows: EMB, 60.0%, 89.2%, 68.2% and 85.3%; OFL, 100%, 91.4%, 56.2% and 100%; KAN, 100%, 97.7%, 60.0% and 100%. Line probe assay showed an excellent agreement (k = 0.93) for INH susceptibility testing when compared to MGIT 960 system while there was good agreement (k = 0.6-0.7) between both methods for RIF, OFL, KAN testing and moderate agreement for EMB (k = 0.5). A high RIF mono-resistance (MGIT 960 33/97 and LPA 43/97) was observed.
Conclusion: LPAs are an efficient and reliable rapid molecular DST assay for rapid susceptibility screening of MDR and XDR-TB. Using LPAs in high MDR/XDR burden countries allows for appropriate and timely treatment, which will reduce transmission rates, morbidity and improve treatment outcomes in patients.
Keywords: Drug-resistance; Ethambutol; Isoniazid; Kanamycin; Line-probe assay; MGIT 960 system; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Ofloxacin; Rifampicin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the Faculty of Health Science Research Ethics, University of Pretoria with protocol number 318/2013 and preceded experimental work.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison between the BACTEC MGIT 960 system and the agar proportion method for susceptibility testing of multidrug resistant tuberculosis strains in a high burden setting of South Africa.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Dec 22;12:369. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-369. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 23259765 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid phenotypic assay of antimycobacterial susceptibility pattern by direct mycobacteria growth indicator tube and phage amplified biological assay compared to BACTEC 460 TB.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007 Mar;87(2):102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2006.05.002. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007. PMID: 17035089
-
Rapid detection of extensively drug-resistant (XDR-TB) strains from multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) cases isolated from smear-negative pulmonary samples in an Intermediate Reference Laboratory in India.Indian J Tuberc. 2016 Jul;63(3):144-148. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2016.07.009. Indian J Tuberc. 2016. PMID: 27865234
-
Accuracy of line probe assays for the diagnosis of pulmonary and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Respir J. 2017 Jan 18;49(1):1601075. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01075-2016. Print 2017 Jan. Eur Respir J. 2017. PMID: 28100546 Free PMC article.
-
Isoniazid resistance in Rifampicin sensitive pulmonary tuberculosis in children and adolescents.Indian J Tuberc. 2024;71 Suppl 1:S145-S148. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2024.05.002. Epub 2024 May 9. Indian J Tuberc. 2024. PMID: 39067947 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation Study of xMAP TIER Assay on a Microsphere-Based Platform for Detecting First-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Resistance.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 19;19(24):17068. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192417068. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554951 Free PMC article.
-
The Performance of the Abbott Real Time MTB RIF/INH Compared to the MTBDRplus V2 for the Identification of MDR-TB Among Isolates.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Sep 28;13:3301-3308. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S247524. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33061477 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of GenoType MTBDRsl assay for detection of second-line drugs and ethambutol resistance directly from sputum specimens of MDR-TB patients in Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 16;16(12):e0261329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261329. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34914803 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of LiquidArray MTB-XDR VER 1.0 for the Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex, Fluoroquinolone, Amikacin, Ethambutol, and Linezolid Susceptibility.Clin Infect Dis. 2025 Aug 1;81(1):159-166. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae614. Clin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39663850 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of LiquidArray MTB-XDR VER1.0 for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, fluoroquinolone, amikacin, ethambutol, and linezolid susceptibility.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 4:rs.3.rs-4841978. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4841978/v2. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Clin Infect Dis. 2025 Aug 1;81(1):159-166. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae614. PMID: 39149464 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organization 2016 . Global Tuberculosis Report 2016. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- Heifets LB, Cangelosi GA. Drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a neglected problem at the turn of the century [State of the Art] Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 1999;3:564–581. - PubMed
-
- Altman DG, Bland JM. Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Underst Stat. 1983;32:307–317.
-
- Nathavitharana RR, Cudahy PGT, Schumacher SG, Steingart KR, Pai M, Denkinger CM. Accuracy of line probe assays for the diagnosis of pulmonary and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2017;49:1601075. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01075-2016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous