R-100 improves pulmonary function and systemic fluid balance in sheep with combined smoke-inhalation injury and Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis
- PMID: 29282084
- PMCID: PMC5745620
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1366-6
R-100 improves pulmonary function and systemic fluid balance in sheep with combined smoke-inhalation injury and Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis
Abstract
Background: Septic shock is a major cause of death in intensive care units around the world . The aim of the study was to investigate whether the novel drug R-100 (a superoxide degradation catalyst and nitric oxide donor) improves pulmonary function in a sheep model of septic shock caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and smoke inhalation.
Methods: Eleven female sheep were prepared surgically and randomly assigned to a treatment group (n = 5) or a control group (n = 6) after inhalation of cooled cotton smoke and airway instillation of live P. aeruginosa (2.5 × 1011 CFU) by bronchoscope under deep anesthesia and analgesia. The treatment group received an intravenous infusion of a total of 80 mg/kg of R-100 diluted in 500 mL of 5% dextrose. The control group was given 500 mL of 5% dextrose. All animals received intravenous lactated Ringer's solution to maintain a hematocrit level at baseline ± 3%. Blood gas and hemodynamics were measured at baseline and then analyzed every 3 h during the 24-h study period. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM.
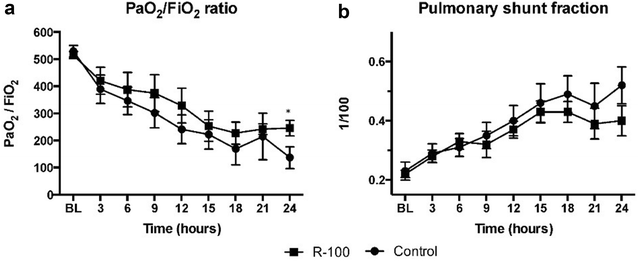
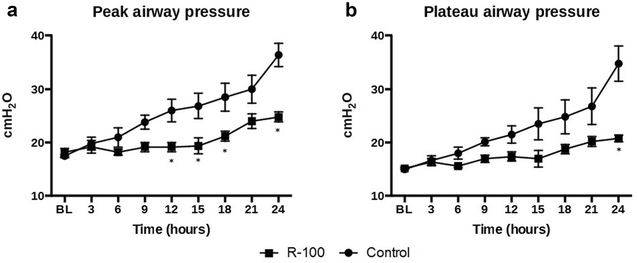
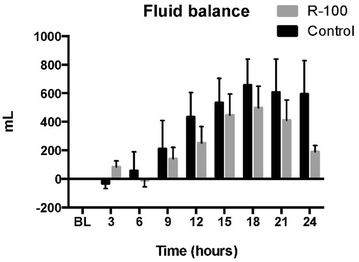
Results: The treated animals showed significant improvement in their pulmonary gas exchange (PaO2/FiO2 ratio at 24 h: 246 ± 29 vs. 90 ± 40 mmHg control, P < 0.05). Pulmonary arterial pressures were reduced in the treated group (24 h: 26 ± 1 vs. 30 ± 2 cm mmHg control, P < 0.05). The treated animals also had an improved total fluid balance after 24 h (190 ± 45/24 h mL vs. 595 ± 234/24 h mL control, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Treatment with R-100 improves pulmonary gas exchange and blood oxygenation, and prevents a fluid imbalance in sheep subjected to smoke inhalation and P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: R-100; Redox; Sepsis; Smoke.
Figures

References
-
- Brown SDARDS. History, definitions, and physiology. Respir Care Clin N Am. 1998;4:567–582. - PubMed
-
- Macarthur H, Couri D, Wilken G, et al. Modulation of serum cytokine levels by a novel superoxide dismutase mimetic, M40401, in an E. coli model of septic shock; correlation with preserved circulating catecholamines. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:237–245. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200301000-00037. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

