LncRNA AK023391 promotes tumorigenesis and invasion of gastric cancer through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 29282102
- PMCID: PMC5745957
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-017-0666-2
LncRNA AK023391 promotes tumorigenesis and invasion of gastric cancer through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction to: LncRNA AK023391 promotes tumorigenesis and invasion of gastric cancer through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 12;39(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01656-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32787877 Free PMC article.
Abstract
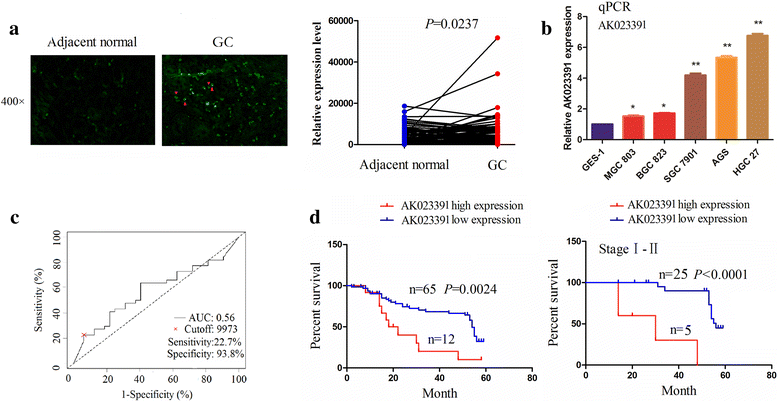
Background: Patients with gastric cancer commonly have a poor prognosis, owing to its invasiveness and distant metastasis. Recent studies have confirmed the pivotal role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumorigenesis and the progression of malignant tumors, including gastric cancer. However, little is known about the molecular mechanism by which lncRNA AK023391 contributes to gastric cancer.
Methods: A lncRNA microarray was used to identify the differentially expressed lncRNA AK023391 in gastric cancer and adjacent normal tissues. In addition, RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was used to investigate the association between AK023391 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Subsequently, a series of in vitro assays and a xenograft tumor model were used to observe the functions of lncRNA AK023391 in gastric cancer cells. A cancer pathway microarray, bioinformatic analysis, western blotting, and immunochemistry were carried out to verify the regulation of AK023391 and its downstream PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
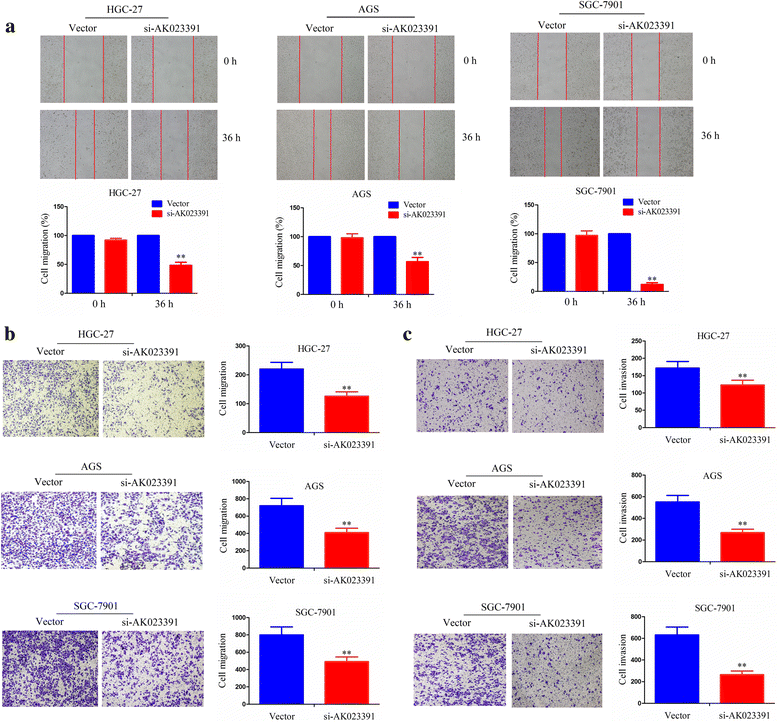
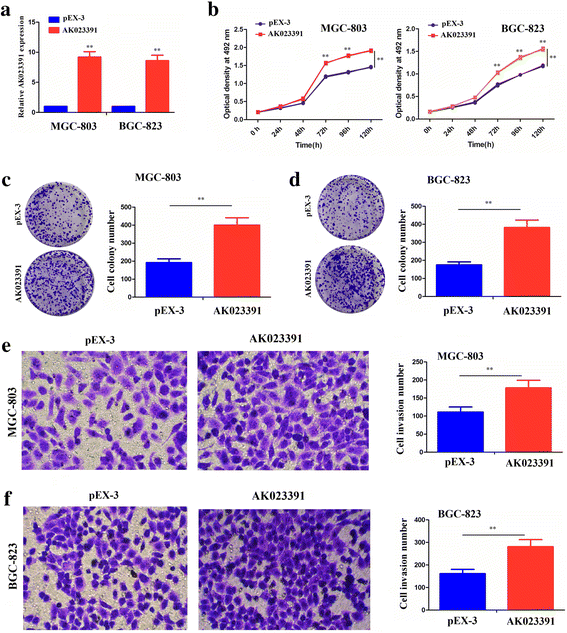
Results: Expression of lncRNA AK023391 was significantly upregulated in gastric cancer samples and cell lines in comparison to adjacent normal tissues, and was positively correlated with poor survival in patients with gastric cancer. The multivariate Cox regression model revealed that AK023391 expression acted as an independent prognostic factor for survival in patients with gastric cancer. Knockdown of AK023391 inhibited cell growth and invasion both in vitro and in vivo, and induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in gastric cancer cells, whereas its overexpression reversed these effects. Mechanistically, PI3K/Akt signaling mediated the NF-κB, FOXO3a, and p53 pathways. Moreover, downstream transcription factors, such as c-myb, cyclinB1/G2, and BCL-6 might be involved in AK023391-induced tumorigenesis in gastric cancer.
Conclusions: The novel oncogenic lncRNA AK023391 in gastric cancer exerts its effects through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, and may act as a potential biomarker for survival in patients with gastric cancer.
Keywords: Akt; Gastric cancer; Invasion; PI3K; lncRNA AK023391.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the Hospital’s Protection of HumanSubjects Committee.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Upregulation of Long Noncoding RNA_GAS5 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Laryngeal Cancer via Regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:1533033821990074. doi: 10.1177/1533033821990074. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33641529 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA AB073614 regulates proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:1230-1237. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.024. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28738539
-
Long noncoding RNA PART1 restrains aggressive gastric cancer through the epigenetic silencing of PDGFB via the PLZF-mediated recruitment of EZH2.Oncogene. 2020 Oct;39(42):6513-6528. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01442-5. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32901105
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the action of carcinogens in gastric cancer with a glimpse into targeted therapy.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Dec;45(6):1073-1117. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00715-3. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 36149600 Review.
-
The long noncoding RNA CRAL reverses cisplatin resistance via the miR-505/CYLD/AKT axis in human gastric cancer cells.RNA Biol. 2020 Nov;17(11):1576-1589. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1709296. Epub 2020 Jan 7. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 31885317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA_CNST Promotes the Tumorigenesis of Osteosarcoma Cells by Sponging miR-421.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720926147. doi: 10.1177/0963689720926147. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32693639 Free PMC article.
-
MCF2L-AS1/miR-874-3p/STAT3 feedback loop contributes to lung adenocarcinoma cell growth and cisplatin resistance.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 29;9(11):e21342. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21342. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37954302 Free PMC article.
-
Survival-Related lncRNA Landscape Analysis Identifies LINC01614 as an Oncogenic lncRNA in Gastric Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 6;12:698947. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.698947. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34691143 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-CASC7 inhibits the proliferation and migration of colon cancer by negatively regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Dec;12(6):2803-2813. doi: 10.21037/jgo-21-643. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35070408 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) HCP5 on Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Related Markers in Gastric Carcinoma Is Partially Reversed by miR-27b-3p.Med Sci Monit. 2020 May 1;26:e921383. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921383. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32357145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leung WK, M-s W, Kakugawa Y, Kim JJ, Yeoh K-g, Goh KL, Wu K-c, D-c W, Sollano J, Kachintorn U, et al. Asia Pacific working group on gastric cancer: screening for gastric cancer in Asia: current evidence and practice. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(3):279–287. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70072-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81573747/the National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- XJ2015033/Hong Kong Scholars Program/International
- 17411966500/Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Western Medicine Guide project/International
- BXJ201737/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine doctoral innovation fund/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

