Design and validation of a disease network of inflammatory processes in the NSG-UC mouse model
- PMID: 29282132
- PMCID: PMC5745765
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1368-4
Design and validation of a disease network of inflammatory processes in the NSG-UC mouse model
Abstract
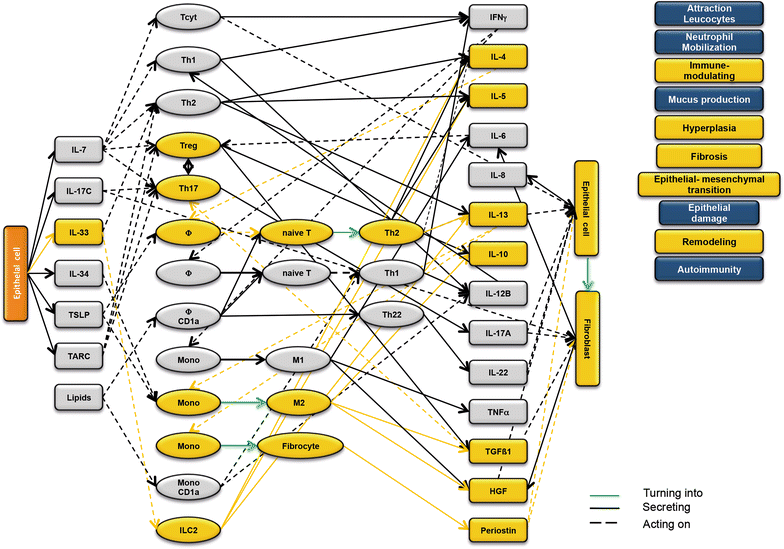
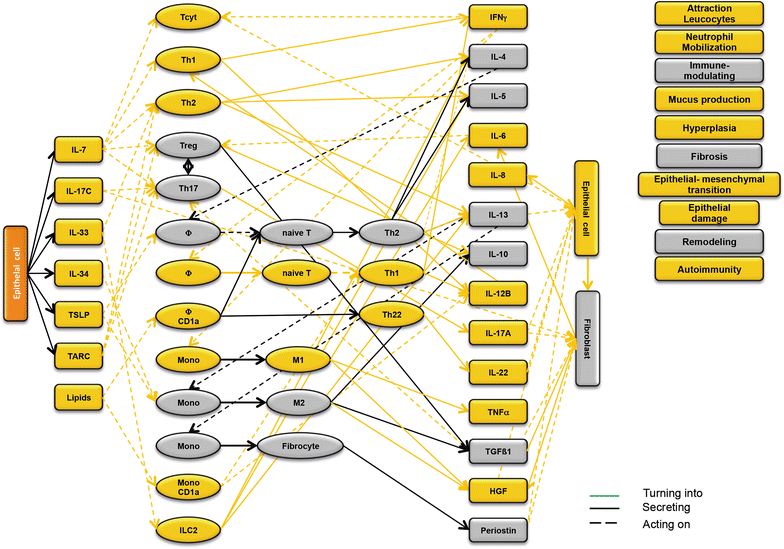
Background: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a highly progressive inflammatory disease that requires the interaction of epithelial, immune, endothelial and muscle cells and fibroblasts. Previous studies suggested two inflammatory conditions in UC-patients: 'acute' and 'remodeling' and that the design of a disease network might improve the understanding of the inflammatory processes. The objective of the study was to design and validate a disease network in the NOD-SCID IL2rγnull (NSG)-UC mouse model to get a better understanding of the inflammatory processes.
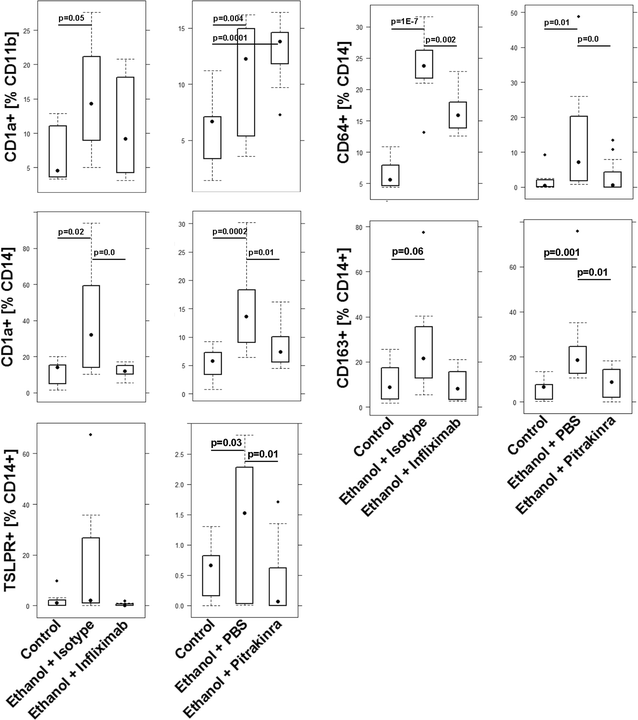
Methods: Leukocytes were isolated from the spleen of NSG-UC mice and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. RT-PCR and RNAseq analysis were performed from distal parts of the colon. Based on these analyses and the effects of interleukins, chemokines and growth factors described in the literature, a disease network was designed. To validate the disease network the effect of infliximab and pitrakinra was tested in the NSG-UC model. A clinical- and histological score, frequencies of human leukocytes isolated from spleen and mRNA expression levels from distal parts of the colon were determined.
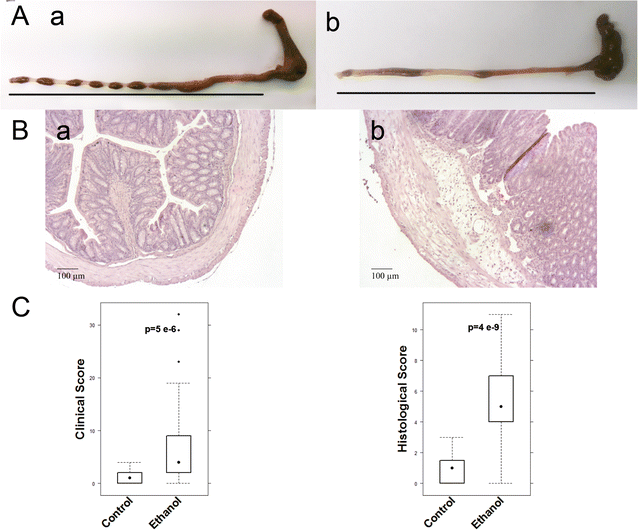
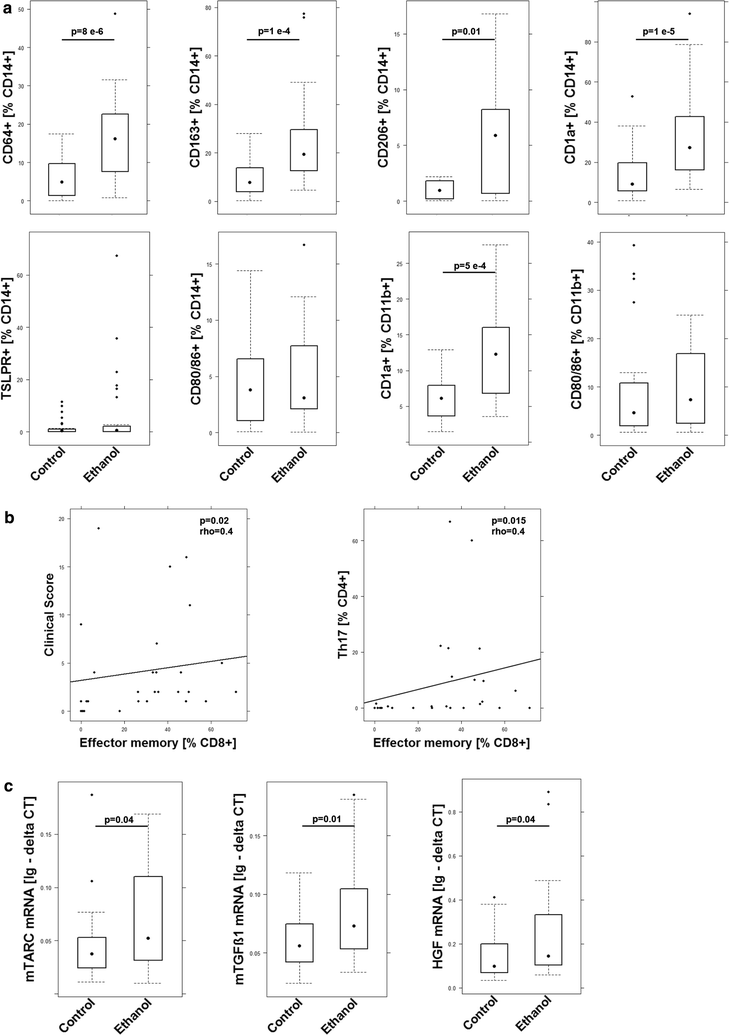
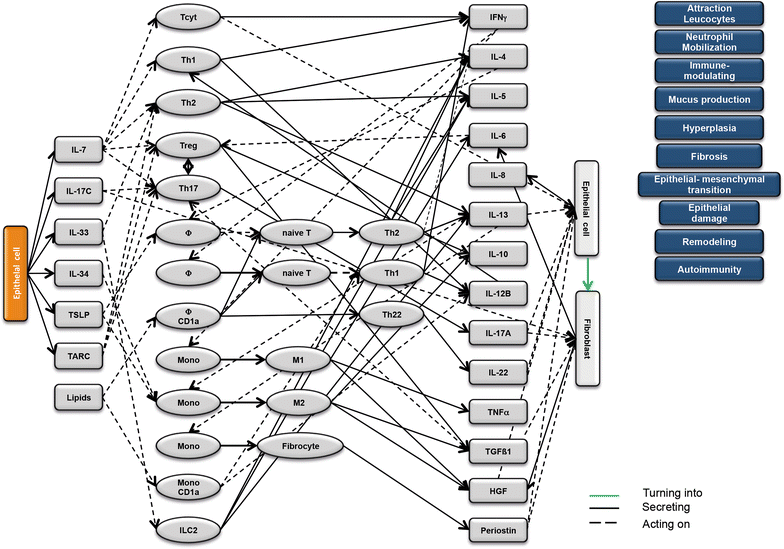
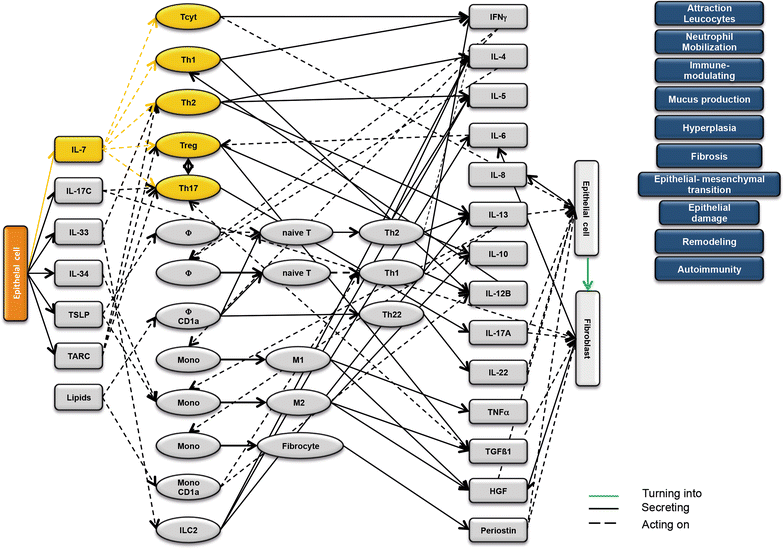
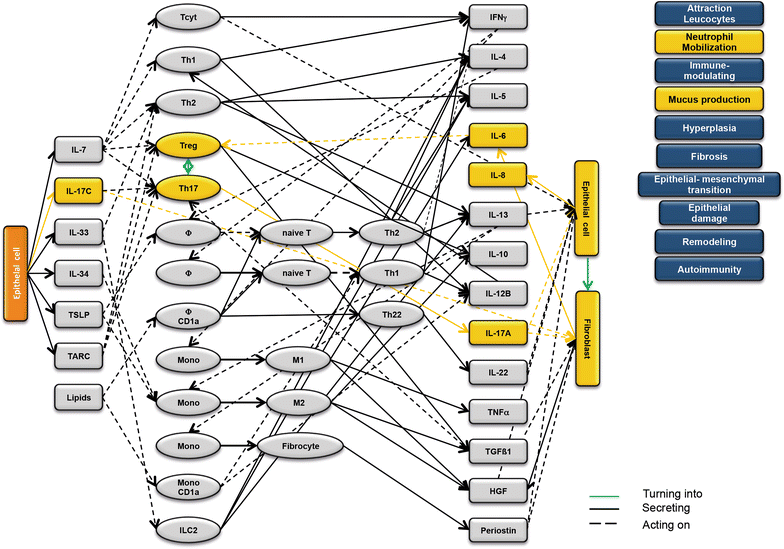
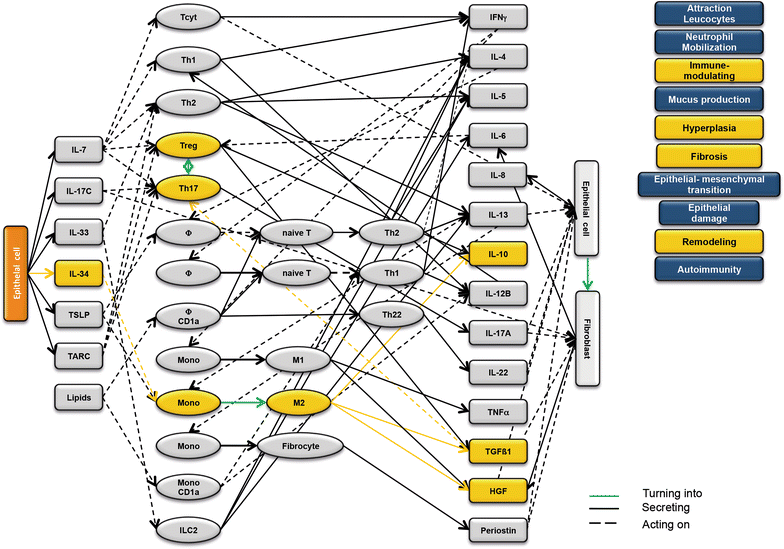
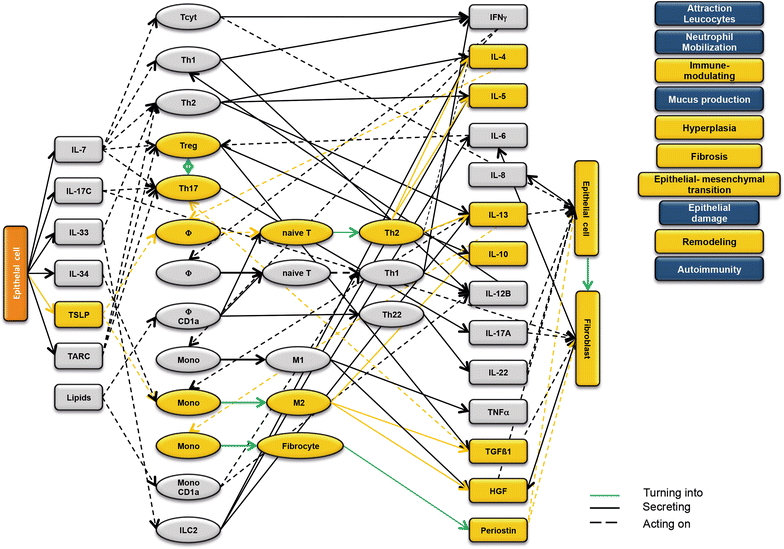
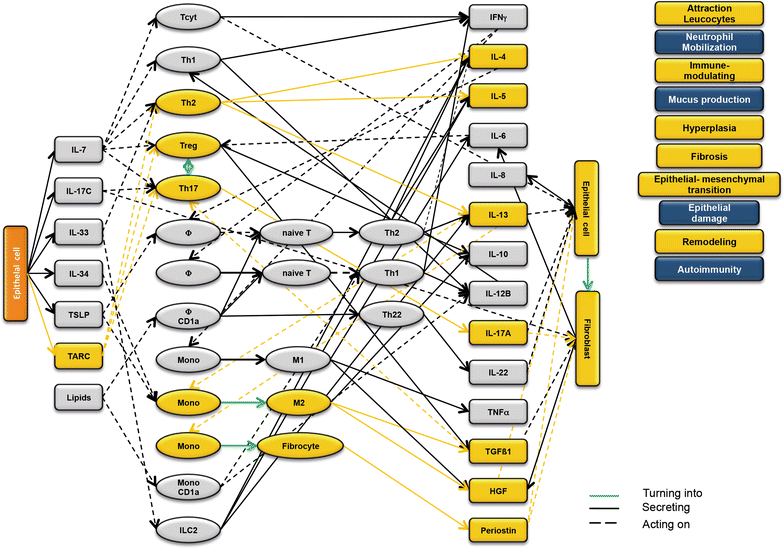
Results: Analysis of leukocytes isolated from the spleen of challenged NSG-UC mice corroborated CD64, CD163 and CD1a expressing CD14+ monocytes, CD1a expressing CD11b+ macrophages and HGF, TARC, IFNγ and TGFß1 mRNA as inflammatory markers. The disease network suggested that a proinflammatory condition elicited by IL-17c and lipids and relayed by cytotoxic T-cells, Th17 cells and CD1a expressing macrophages and monocytes. Conversely, the remodeling condition was evoked by IL-34 and TARC and promoted by Th2 cells and M2 monocytes. Mice benefitted from treatment with infliximab as indicated by the histological- and clinical score. As predicted by the disease network infliximab reduced the proinflammatory response by suppressing M1 monocytes and CD1a expressing monocytes and macrophages and decreased levels of IFNγ, TARC and HGF mRNA. As predicted by the disease network inflammation aggravated in the presence of pitrakinra as indicated by the clinical and histological score, elevated frequencies of CD1a expressing macrophages and TNFα and IFNγ mRNA levels.
Conclusions: The combination of the disease network and the NSG-UC animal model might be developed into a powerful tool to predict efficacy or in-efficacy and potential mechanistic side effects.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Disease network; Inflammatory bowel disease; NSG; NSG-UC; Ulcerative colitis.
Figures




References
-
- Heller F, Florian P, Bojarski C, Richter J, Christ M, Hillenbrand B, Mankertz J, Gitter AH, Burgel N, Fromm M, et al. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:550–564. doi: 10.1016/j.gastro.2005.05.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

