Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach in a Case of Severe Post-Traumatic Hyphema with Subtotal Iridodialysis
- PMID: 29282400
- PMCID: PMC5731096
- DOI: 10.1159/000480726
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach in a Case of Severe Post-Traumatic Hyphema with Subtotal Iridodialysis
Abstract
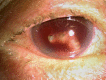
Purpose: To report our diagnostic ultrasound-based approach and surgical strategy in a case of severe blunt trauma with complete hyphema, 270° iris disinsertion, and traumatic subluxated cataract.
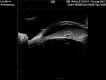
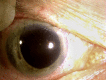
Case report: A 70-year-old male was referred to our hospital for a blunt trauma in his right eye. A complete examination revealed visual acuity consisting in light perception, a complete hyphema, and an intraocular pressure of 45 mm Hg with moderate pain. Our diagnostic approached was ultrasound based with B-scan examination showing some vitreous hemorrhage and ultrasound biomicroscopy showing a large iris disinsertion of 270° with the iris entirely dislocated in the inferior sector of the anterior chamber. The patient was hospitalized and a systemic and topical treatment was started to lower intraocular pressure. Our surgery consisted in a single-step approach with removal of traumatic cataract with scleral fixation of an intraocular lens and iridoplasty.
Conclusion: In our patient, the single-step surgery, supported by anterior and posterior ultrasound imaging, achieved a satisfactory anatomical and functional outcome.
Keywords: Hyphema; Iridodialysis; Iridoplasty; Traumatic cataract surgery; Ultrasound; Ultrasound biomicroscopy.
Figures



References
-
- Berinstein DM, Gentile RC, Sidoti PA, Stegman Z, Tello C, Liebmann JM, Ritch R. Ultrasound biomicroscopy in anterior ocular trauma. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1997;28:201–207. - PubMed
-
- Genovesi-Ebert F, Rizzo S, Chiellini S, Romani A, Gabbriellini G, Sartini MS, Nardi M. Ultrasound biomicroscopy in the assessment of penetrating or blunt anterior-chamber trauma. Ophthalmologica. 1998;212((suppl 1)):6–7. - PubMed
-
- Bansal S, Gunasekeran DV, Ang B, Lee J, Khandelwal R, Sullivan P, Agrawal R. Controversies in the pathophysiology and management of hyphema. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016;61:297–308. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

