Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation Procedures
- PMID: 29283397
- PMCID: PMC5793105
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10010018
Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation Procedures
Abstract
Injections of botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) are prescribed by clinicians for a variety of disorders that cause over-activity of muscles; glands; pain and other structures. Accurately targeting the structure for injection is one of the principle goals when performing BoNTs procedures. Traditionally; injections have been guided by anatomic landmarks; palpation; range of motion; electromyography or electrical stimulation. Ultrasound (US) based imaging based guidance overcomes some of the limitations of traditional techniques. US and/or US combined with traditional guidance techniques is utilized and or recommended by many expert clinicians; authors and in practice guidelines by professional academies. This article reviews the advantages and disadvantages of available guidance techniques including US as well as technical aspects of US guidance and a focused literature review related to US guidance for chemodenervation procedures including BoNTs injection.
Keywords: anatomic localization; botulinum neurotoxin; botulinum toxin; chemodenervation; electrical stimulation; electromyography; guidance; motor points; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Alter has received royalties from Demos Medical Publishing.
Figures
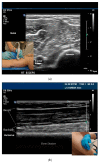
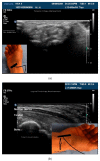
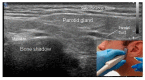

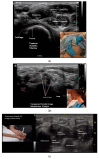



Comment in
-
Comment on Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation Procedures. Toxins 2017, 10, 18-Quintessential Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Toxin Injections-Muscle Innervation Zone Targeting Revisited.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;10(10):396. doi: 10.3390/toxins10100396. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274173 Free PMC article.
-
Reply to Comment on Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation Procedures. Toxins 2018, 10, 18-Quintessential Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Toxin Injections.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;10(10):400. doi: 10.3390/toxins10100400. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274231 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Management of Anterocapitis and Anterocollis: A Novel Ultrasound Guided Approach Combined with Electromyography for Botulinum Toxin Injection of Longus Colli and Longus Capitis.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 30;12(10):626. doi: 10.3390/toxins12100626. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33008043 Free PMC article.
-
Comment on Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation Procedures. Toxins 2017, 10, 18-Quintessential Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Toxin Injections-Muscle Innervation Zone Targeting Revisited.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;10(10):396. doi: 10.3390/toxins10100396. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274173 Free PMC article.
-
Ergonomic Recommendations in Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation for Spasticity: An International Expert Group Opinion.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Mar 31;13(4):249. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040249. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reply to Comment on Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Neurotoxin Chemodenervation Procedures. Toxins 2018, 10, 18-Quintessential Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Botulinum Toxin Injections.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;10(10):400. doi: 10.3390/toxins10100400. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274231 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin injection techniques for the management of adult spasticity.PM R. 2015 Apr;7(4):417-27. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2014.09.021. Epub 2014 Oct 8. PM R. 2015. PMID: 25305369 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Anterocapitis and Anterocollis: A Novel Ultrasound Guided Approach Combined with Electromyography for Botulinum Toxin Injection of Longus Colli and Longus Capitis.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 30;12(10):626. doi: 10.3390/toxins12100626. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33008043 Free PMC article.
-
Incobotulinum Toxin A with a One-year Long-lasting Effect for Trapezius Contouring and Superior Efficacy for the Treatment of Trapezius Myalgia.J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022 Apr-Jun;15(2):168-174. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_68_21. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022. PMID: 35965898 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injections for Hand Spasticity: A Technical Guide for the Dorsal Approach.Toxins (Basel). 2025 May 3;17(5):225. doi: 10.3390/toxins17050225. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40423308 Free PMC article.
-
In-Plane Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injection to Lumbrical and Interosseus Upper Limb Muscles: Technical Report.Cureus. 2023 Sep 12;15(9):e45073. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45073. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37842408 Free PMC article.
-
AbobotulinumtoxinA provides flexibility for the treatment of cervical dystonia with 500 U/1 mL and 500 U/2 mL dilutions.Clin Park Relat Disord. 2021 Nov 20;5:100115. doi: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2021.100115. eCollection 2021. Clin Park Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34888518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter K.K., Nahab F.A. Comparison of Botulinum Neurotoxin Products. In: Alter K.K., Wilson N.A., editors. Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Manual. Demos Medical Publishing; New York, NY, USA: 2015. pp. 10–18.
-
- Lungu C., Ahmad O.F. Seminars in Neurology. Volume 36. Thieme Medical Publishers; Stuttgart, Germany: 2016. Update on the Use of Botulinum Toxin Therapy for Focal and Task-Specific Dystonias; pp. 41–46. - PubMed
-
- Simpson D.M., Hallett M., Ashman E.J., Comella C.L., Green M.V., Gronseth G.S., Armstrong M.J., Gloss D., Potrebic S., Jankovic J., et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2016;86:1818–1826. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

