Omentin-A Novel Adipokine in Respiratory Diseases
- PMID: 29283409
- PMCID: PMC5796023
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19010073
Omentin-A Novel Adipokine in Respiratory Diseases
Abstract
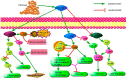
Adipokines, secreted by the adipose tissue, are extensively involved in the regulation and maintenance of various physiological and pathological processes, including insulin sensitivity, energy expenditure, glucose and lipid metabolism, inflammatory activity, neuroendocrine activity, immunity, cancer, homeostasis, angiogenesis, cardiovascular function, breeding and bone metabolism, and all functions of the endocrine-reproductive system axis. Omentin is a recently identified adipokine, which has become a research hotspot due to its pleiotropic effects on various diseases. However, the specific receptor for omentin has not been identified so far. In this study, we report that omentin levels fluctuate in various diseases. In addition, we have focused on the pleiotropic roles of omentin in pulmonary diseases, as it may act as a biomarker for malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) and is related to disease severity. Omentin may play significant roles in other pulmonary diseases, such as asthma, obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This review summarizes the advances in current knowledge and future trends, which may provide a concise and general view on omentin and its effects on pulmonary biology.
Keywords: ARDS; COPD; MPM; OSAS; PAH; adipokines; adipose tissue; asthma; omentin; respiratory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

