The Effects of Berberine on Concanavalin A-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) in Mice and the Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate (AMP)-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Pathway
- PMID: 29283990
- PMCID: PMC5753750
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.907377
The Effects of Berberine on Concanavalin A-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) in Mice and the Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate (AMP)-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Pathway
Abstract
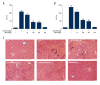
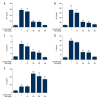
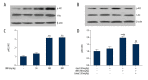
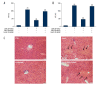
BACKGROUND Berberine, a herbal extract, has been reported to protect against inflammatory disorders. The adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway can be activated by berberine and inhibited by the synthetic, reversible AMP-competitive inhibitor, Compound C. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of berberine on concanavalin A (Con A)-induced autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) in mice via the AMPK pathway. MATERIAL AND METHODS BALB/c mice were treated with berberine, with or without Compound C, followed by treatment with Con A. Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were measured. Liver tissue histology was performed to evaluate hepatic injury and AIH. Cytokine levels in serum and hepatic tissue were measured by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) and used quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Levels of phosphorylated acetyl coenzyme-A carboxylase (ACC), representing AMPK activation, were detected by Western blotting. RESULTS Serum ALT and AST levels were significantly reduced by berberine (100 and 200 mg/kg/day) in mice with Con A-induced hepatitis. Berberine also reduced Con A-induced hepatocyte swelling, cell death, and infiltration of leukocytes. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interferon (IF)-gamma, interleukin (IL)-2, and IL-1beta were reduced by berberine pre-treatment; levels of serum IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, was elevated. These protective effects of berberine on Con-A-induced AIH were reversed by treatment with Compound C. CONCLUSIONS In a murine model of Con A-induced AIH, berberine treatment reduced hepatic injury via activation of the AMPK pathway. Further studies are recommended to determine the potential therapeutic role for berberine in AIH.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rosmarinic Acid Protects Mice from Concanavalin A-Induced Hepatic Injury through AMPK Signaling.Biol Pharm Bull. 2020 Nov 1;43(11):1749-1759. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b20-00477. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 32893253
-
Selective inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme attenuates liver toxicity in a murine model of concanavalin A induced auto-immune hepatitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Oct;17(2):229-36. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23816535
-
Emodin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibiting activation of the p38 MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(4):1557-70. doi: 10.1159/000373971. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25792514
-
A review of the utility of tacrolimus in the management of adults with autoimmune hepatitis.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;54(1):76-80. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2018.1551498. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30650311 Review.
-
Berberine Exerts Anti-cancer Activity by Modulating Adenosine Monophosphate- Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/ Protein Kinase B (PI3K/AKT) Signaling Pathways.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(4):565-574. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200928155728. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 32988344
Cited by
-
Berberine and its derivatives represent as the promising therapeutic agents for inflammatory disorders.Pharmacol Rep. 2022 Apr;74(2):297-309. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00348-7. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Pharmacol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35083737 Review.
-
Berberine alleviates concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice by modulating the gut microbiota.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Mar 11;8(4):e0381. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000381. eCollection 2024 Apr 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38466881 Free PMC article.
-
Summary of Natural Products Ameliorate Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury: Structures, Sources, Pharmacological Effects, and Mechanisms of Action.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 25;10(2):228. doi: 10.3390/plants10020228. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33503905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hepatoprotection by Oleanolic Acid Preconditioning: Focusing on PPARα Activation.PPAR Res. 2018 Apr 2;2018:3180396. doi: 10.1155/2018/3180396. eCollection 2018. PPAR Res. 2018. PMID: 29805439 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory impacts of berberine on activation of autoreactive T cells in autoimmune inflammation.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(23):13573-13588. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16049. Epub 2020 Nov 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33135395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fei M, Xie Q, Zou Y, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid protects mice against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by modulating cytokine secretion and reducing reactive oxygen species generation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;35:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Xue J, Chen F, Wang J, et al. Emodin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibiting activation of the p38 MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:1557–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

