Pembrolizumab in Asia-Pacific patients with advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Analyses from KEYNOTE-012
- PMID: 29284202
- PMCID: PMC5834807
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13480
Pembrolizumab in Asia-Pacific patients with advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Analyses from KEYNOTE-012
Abstract
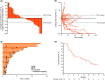
KEYNOTE-012 was a phase Ib, multicohort study designed to investigate efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab in advanced solid tumors. Results from the subset of patients with recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) from the Asia-Pacific region are reported. Patients with recurrent/metastatic HNSCC, measurable disease (RECIST version 1.1), and ECOG performance status (PS) 0-1 were eligible for enrollment in the HNSCC expansion cohort. Patients received pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks. Response was assessed every 8 weeks. Co-primary end-points were safety and overall response rate (RECIST version 1.1, central review). Secondary end-points included overall survival and response duration. Patients enrolled at any of the five centers throughout the Asia-Pacific region were included in these analyses. Twenty-six patients with HNSCC from the Asia-Pacific region received pembrolizumab. The median age was 62 years, 65% of patients had ECOG PS 1, and 62% had received two or more prior therapies for recurrent/metastatic disease. Sixteen (62%) patients experienced a treatment-related adverse event of any grade, including two (8%) patients who experienced one or more events of grade 3 severity. No treatment-related deaths occurred. The overall response rate was 19% (95% confidence interval, 7%-39%). After a median follow-up of 12 months (range, 2-21 months), a median response duration was not reached (range, 6 to 17+ months); four of five responses lasted ≥6 months. Median overall survival was 11.6 months (95% confidence interval, 4.7-17.7 months). Pembrolizumab was well tolerated and had durable antitumor activity in patients with HNSCC from the Asia-Pacific region. (Trial registration no. NCT01848834.).
Keywords: Asia-Pacific; PD-1; PD-L1; Pembrolizumab; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pembrolizumab for recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer: equally promising for Asian patients?Ann Transl Med. 2019 Mar;7(Suppl 1):S14. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.01.46. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31032295 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Immunotherapeutic strategies in patients with advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Mar;7(Suppl 1):S22. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.01.72. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31032302 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359‐E386. - PubMed
-
- Gupta B, Johnson NW, Kumar N. Global epidemiology of head and neck cancers: a continuing challenge. Oncology. 2016;91:13‐23. - PubMed
-
- Denaro N, Russi EG, Adamo V, Merlano MC. State‐of‐the‐art and emerging treatment options in the management of head and neck cancer: news from 2013. Oncology. 2014;86:212‐229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

