Transcriptome analysis reveals key roles of AtLBR-2 in LPS-induced defense responses in plants
- PMID: 29284410
- PMCID: PMC5747113
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-4372-4
Transcriptome analysis reveals key roles of AtLBR-2 in LPS-induced defense responses in plants
Abstract
Background: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Gram-negative bacteria cause innate immune responses in animals and plants. The molecules involved in LPS signaling in animals are well studied, whereas those in plants are not yet as well documented. Recently, we identified Arabidopsis AtLBR-2, which binds to LPS from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (pLPS) directly and regulates pLPS-induced defense responses, such as pathogenesis-related 1 (PR1) expression and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. In this study, we investigated the pLPS-induced transcriptomic changes in wild-type (WT) and the atlbr-2 mutant Arabidopsis plants using RNA-Seq technology.
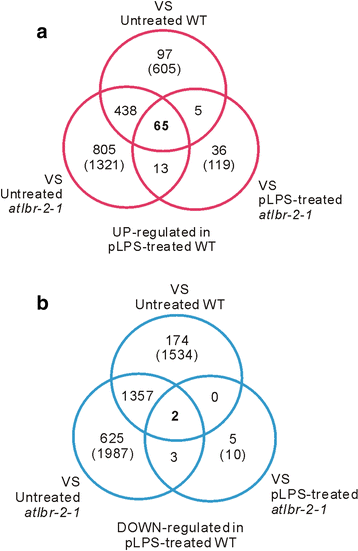
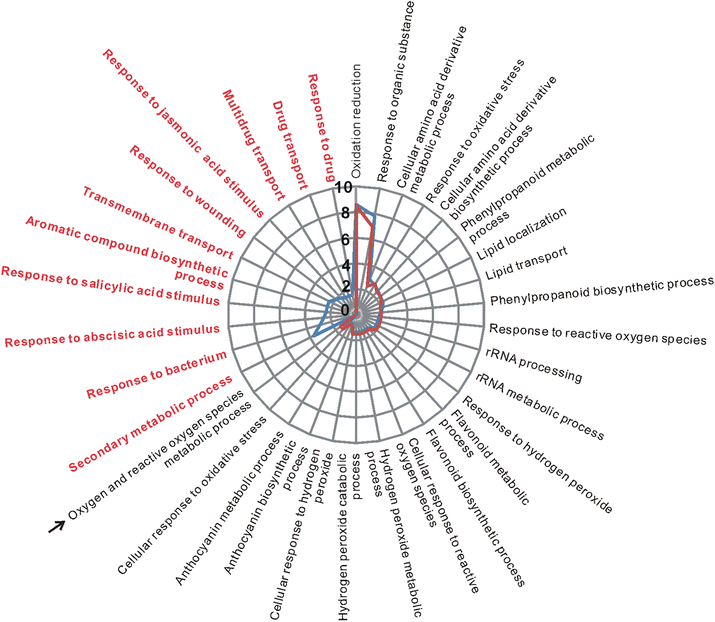
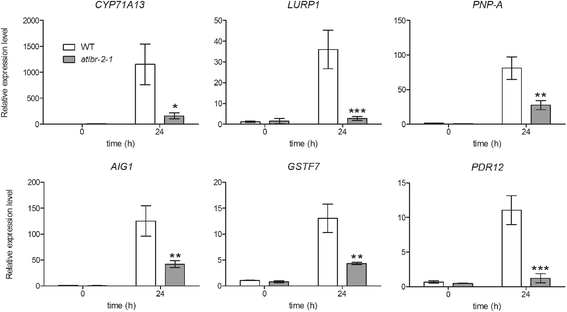
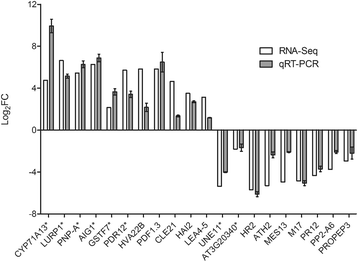
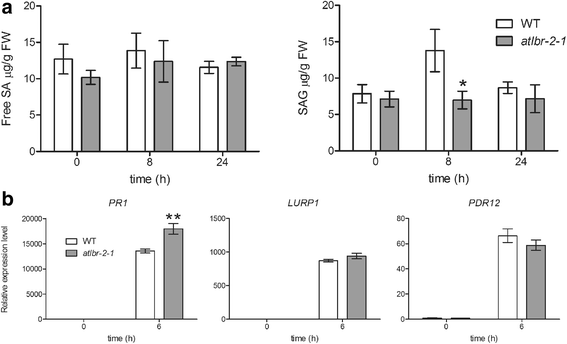
Results: RNA-Seq data analysis revealed that pLPS treatment significantly altered the expression of 2139 genes, with 605 up-regulated and 1534 down-regulated genes in WT. Gene ontology (GO) analysis on these genes showed that GO terms, "response to bacterium", "response to salicylic acid (SA) stimulus", and "response to abscisic acid (ABA) stimulus" were enriched amongst only in up-regulated genes, as compared to the genes that were down-regulated. Comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes between WT and the atlbr-2 mutant revealed that 65 genes were up-regulated in WT but not in the atlbr-2 after pLPS treatment. Furthermore, GO analysis on these 65 genes demonstrated their importance for the enrichment of several defense-related GO terms, including "response to bacterium", "response to SA stimulus", and "response to ABA stimulus". We also found reduced levels of pLPS-induced conjugated SA glucoside (SAG) accumulation in atlbr-2 mutants, and no differences were observed in the gene expression levels in SA-treated WT and the atlbr-2 mutants.
Conclusion: These 65 AtLBR-2-dependent up-regulated genes appear to be important for the enrichment of some defense-related GO terms. Moreover, AtLBR-2 might be a key molecule that is indispensable for the up-regulation of defense-related genes and for SA signaling pathway, which is involved in defense against pathogens containing LPS.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; Defense response; Lipopolysaccharide; Plant immunity; RNA-Seq; Salicylic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of Arabidopsis WRKY25 transcription factor in plant defense against Pseudomonas syringae.BMC Plant Biol. 2007 Jan 10;7:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-7-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17214894 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide- induced AtAO3 differentially regulates plant defense and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Dec 30;19(1):602. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2210-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31888479 Free PMC article.
-
The GH3 acyl adenylase family member PBS3 regulates salicylic acid-dependent defense responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jun;144(2):1144-56. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.097691. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17468220 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylic acid: biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019 Aug;50:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 30901692 Review.
-
The effects of ozone on antioxidant responses in plants.Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;23(3):480-8. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(97)00108-1. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997. PMID: 9214586 Review.
Cited by
-
Perception of unrelated microbe-associated molecular patterns triggers conserved yet variable physiological and transcriptional changes in Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis.Hortic Res. 2020 Nov 1;7(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00410-0. Hortic Res. 2020. PMID: 33328480 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Membrane-Associated Proteins Identified in Arabidopsis Wild Type, lbr2-2 and bak1-4 Mutants Treated with LPSs from Pseudomonas syringae and Xanthomonas campestris.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;12(6):606. doi: 10.3390/membranes12060606. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736313 Free PMC article.
-
Speaking the language of lipids: the cross-talk between plants and pathogens in defence and disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(9):4399-4415. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03791-0. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33638652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects of Gene Knockouts in the Functional Study of MAMP-Triggered Immunity: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 6;21(7):2540. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072540. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32268496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of MAMP-Responsive Plasma Membrane-Associated Proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana Following Challenge with Different LPS Chemotypes from Xanthomonas campestris.Pathogens. 2020 Sep 25;9(10):787. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9100787. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32992883 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

