How to avoid unintended valgus alignment in distal femoral derotational osteotomy for treatment of femoral torsional malalignment - a concept study
- PMID: 29284442
- PMCID: PMC5747093
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1904-7
How to avoid unintended valgus alignment in distal femoral derotational osteotomy for treatment of femoral torsional malalignment - a concept study
Abstract
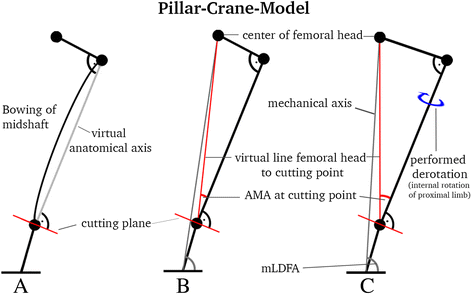
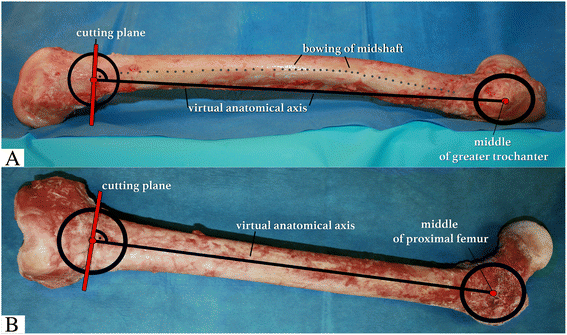
Background: Defining the optimal cutting plane for derotational osteotomy at the distal femur for correction of torsion in cases of patellofemoral instability is still challenging. This preliminary study investigates changes of frontal alignment by a simplified trigonometrical model and demonstrates a surgical guidance technique with the use of femur cadavers. The hypothesis was that regardless of midshaft bowing, a cutting plane perpendicular to the virtual anatomic shaft axis avoids unintended valgus malalignment due to derotation.
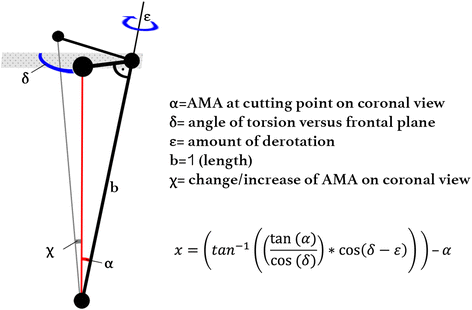
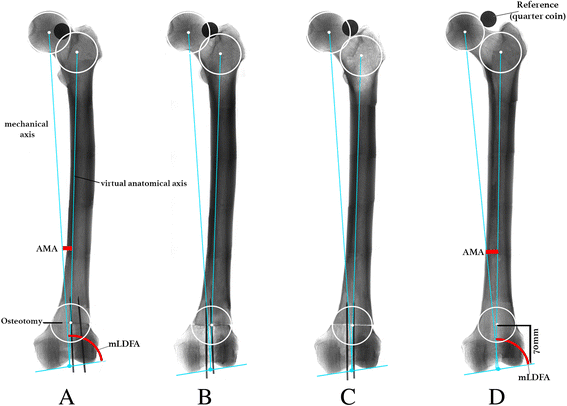
Methods: A novel mathematical model, called the Pillar-Crane-Model, was developed to forecast changes on frontal alignment of the femur when a perpendicular cutting plane to the virtual anatomical shaft was chosen. As proof of concept, eight different torsion angles were assessed on two human cadaver femora (left and right). A single cut distal femoral osteotomy perpendicular to the virtual anatomical shaft was performed. Frontal plane alignment (mLDFA, aLDFA, AMA) was radiographically analyzed before and after rotation by 0°, 10°, 20°, and 30°. Measurements were compared to the model.
Results: The trigonometrical equation from the Pillar-Crane-Model provides mathematical proof that slight changes into varus occur, seen by an increase in AMA and mLDFA, when the cutting plane is perpendicular to the virtual anatomical shaft axis. A table with standardized values is provided. Exemplarily, the specimens showed a mean increase of AMA from 4.8° to 6.3° and mLDFA from 85.2° to 86.7 after derotation by 30°. Throughout the derotation procedure, aLDFA remained at 80.4° ± 0.4°SD.
Conclusions: With the use of this model for surgical guidance and anatomic reference, unintended valgus changes on frontal malalignment can be avoided. When the cutting plane is considered to be perpendicular to the virtual anatomical shaft from a frontal and lateral view, a slight increase of mLDFA results when a derotational osteotomy of the distal femur is performed.
Keywords: Distal femoral derotational osteotomy; Mechanical anatomical axis; Patellofemoral instability; Torsion correction; Valgus-varus alignment.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Florian B. Imhoff, MD; Specialist Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery; German Board Certified.
Currently: Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Uconn Health, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery.
263 Farmington Avenue, Farmington, CT 06030, USA.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was reported to the institutional review board (IRB) of the Uconn Health, University of Connecticut, and it was documented that no IRB approval was required (de-identified specimen do not constitute human subjects research). Specimen had been obtained from MedCure (MedCure, Inc., Cumberland, RI, USA). According to the distributors information, consent was obtained from the patient before death.
Consent for publication
not applicable
Competing interests
Authors Imhoff FB, Scheiderer B, Zakko P, Obopilwe E, and Liska F declare that they have no conflict of interest. Author Imhoff AB is a consultant for Arthrosurface, Arthrex, and mediBayreuth. Author Mazzocca AD is a consultant for Orthofix and Arthrex and receives research grants from Arthrex, Author Arciero RA received an educational and institutional grant from Arthrex and is a consultant for Biorez, Author Beitzel K is a consultant for Arthrex and is a member of the editorial board for this journal.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Eckhoff DG, Montgomery WK, Kilcoyne RF, Stamm ER. Femoral morphometry and anterior knee pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;302:64–68. - PubMed
-
- Nelitz M, Dreyhaupt J, Williams SR, Dornacher D. Combined supracondylar femoral derotation osteotomy and patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellar dislocation and severe femoral anteversion syndrome: surgical technique and clinical outcome. Int Orthop. 2015;39:2355–2362. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2859-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

