Evaluation of the Accuracy of Cone Beam Computed Tomography for Immediate Implant Placement- A Case Report
- PMID: 29284979
- PMCID: PMC5731030
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_94_17
Evaluation of the Accuracy of Cone Beam Computed Tomography for Immediate Implant Placement- A Case Report
Abstract
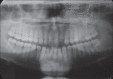
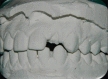
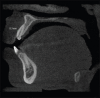
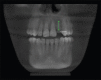
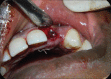
Diagnostic imaging acts as a distinctive method in analyzing and drawing in the appropriate treatment protocol for any procedure. Pertaining to immediate implant placement, determining the bone width and height plays a vital role in the success of the implant therapy. This visualization of the measurements done preoperatively will enhance the treatment by reducing the overall time span of the procedure. Currently, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) plays a significant role in the preoperative determination of the measurements of the tooth and the bone. This case report is regarding, a 27-year-old male patient reporting to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at Madha Dental College and Hospital, with a chief complaint of fractured crown in relation to the upper left front tooth region. On clinical examination, there was the presence of an endodontically failed and fractured crown in relation to 22. With the interpretation of clinical and radiographic examination, the tooth was categorized under unfavorable prognosis. The patient was given a detailed description of the various treatment procedures available pertaining to that present condition, along with immediate implant placement procedure. Since the patient was young and conscious about his esthetics and accuracy, he opted for placement of immediate implant followed by extraction of the tooth. To accurately determine the length and width, the tooth and socket measurements were preoperatively measured by CBCT. This article evaluates the accuracy of CBCT by comparing the clinical quantity of bone and dimensions of tooth to be extracted and alveolar socket.
Keywords: Bone expanders; cone beam computed tomography; immediate implant; periotome.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Schwartz-Arad D, Chaushu G. The ways and wherefores of immediate placement of implants into fresh extraction sites: A literature review. J Periodontol. 1997;68:915–23. - PubMed
-
- Werbitt MJ, Goldberg PV. The immediate implant: Bone preservation and bone regeneration. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1992;12:206–17. - PubMed
-
- Rosenquist B, Grenthe B. Immediate placement of implants into extraction sockets: Implant survival. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996;11:205–9. - PubMed
-
- Wanschitz F, Birkfellner W, Watzinger F, Schopper C, Patruta S, Kainberger F, et al. Evaluation of accuracy of computer-aided intraoperative positioning of endosseous oral implants in the edentulous mandible. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Lazzara RJ. Immediate implant placement into extraction sites: Surgical and restorative advantages. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1989;9:332–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

