Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of PI3K/AKT and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
- PMID: 29285087
- PMCID: PMC5740531
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5242
Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of PI3K/AKT and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
Abstract
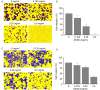
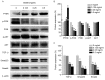
Metastasis is one of the most aberrant behaviors of cancer cells. Patients with cancers, including colorectal cancer (CRC), have a higher risk of tumor recurrence and cancer-related mortality once metastasis is diagnosed. Existing treatment strategies fail to cure cancer mostly due to the onset of metastasis. Therefore, metastasis remains a challenge in cancer treatment. Some complementary and alternative medical therapies using traditional Chinese medicine have been demonstrated to be clinically effective in cancer treatment. Scutellaria barbata D. Don (SB) is a promising medicinal herb. It was previously reported that the ethanol extract of SB (EESB) is able to promote apoptosis, and inhibit cell proliferation and angiogenesis in human colon cancer cells. However, the anticancer effect of SB and the underlying mechanism require further investigation, particularly its role against metastasis. To further elucidate the antimetastatic effect of SB, MTT and Transwell assays were used in the present study to evaluate the effect of EESB on the proliferation, migration and invasion of the CRC cell line HCT-8. In addition, western blot analysis was performed to detect the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), cadherins and other metastasis-associated proteins. EESB significantly reduced HCT-8 cell viability and attenuated the migration and invasion ability of HCT-8 cells in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, EESB decreased the expression of MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3/10, MMP-9 and MMP-13, and proteins in the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/Smad pathways, but not the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related factors E-cadherin and N-cadherin. In conclusion, the results suggested that SB inhibits CRC cell metastasis via the suppression of PI3K/AKT and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways, which may represent a mechanism by which SB exerts an anticancer effect.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT pathway; Scutellaria barbata D. Don; TGF-β/Smad pathway; colorectal cancer; invasion; migration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese Medicines as Effective Reversals of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Induced-Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer: Molecular Targets and Mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 4;13:842295. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.842295. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35308223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits colorectal cancer growth via suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Nov;23(11):858-863. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2775-3. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 29080197
-
Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by regulating PI3K/AKT pathway.Oncol Rep. 2017 Oct;38(4):2293-2300. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5892. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849113
-
Scutellaria Barbata D Don Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth via Suppression of Multiple Signaling Pathways.Integr Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13(3):240-8. doi: 10.1177/1534735413508811. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Integr Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24231788
-
The Anticancer Properties of Silibinin: Its Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Effect in Breast Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(15):1787-1796. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666191220142741. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31858905 Review.
Cited by
-
Crocetin suppresses the growth and migration in HCT-116 human colorectal cancer cells by activating the p-38 MAPK signaling pathway.Res Pharm Sci. 2020 Nov 27;15(6):592-601. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.301344. eCollection 2020 Dec. Res Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33828602 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal circCOL1A1 promotes angiogenesis via recruiting EIF4A3 protein and activating Smad2/3 pathway in colorectal cancer.Mol Med. 2023 Nov 8;29(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00747-x. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37940881 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicines as Effective Reversals of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Induced-Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer: Molecular Targets and Mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 4;13:842295. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.842295. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35308223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zearalenone Exposure Enhanced the Expression of Tumorigenesis Genes in Donkey Granulosa Cells via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Front Genet. 2018 Jul 31;9:293. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00293. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30108608 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Key miRNAs for Colon Cancer Based on miRNA-Gene Integration Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Dec 5;16:5703-5718. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S440340. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 38077476 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
