HMGB1, TGF-β and NF-κB are associated with chronic allograft nephropathy
- PMID: 29285170
- PMCID: PMC5740786
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5319
HMGB1, TGF-β and NF-κB are associated with chronic allograft nephropathy
Abstract
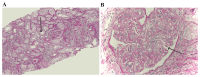
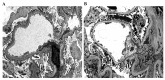
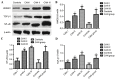
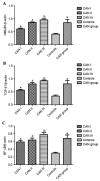
The present study aimed to investigate the association between high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and chronic allograft nephropathy (CAN) and to identify the clinical significance of HMGB1, TGF-β1, NF-κB on patients with CAN. Between September 2012 and November 2014, 27 patients with CAN diagnosed by biopsy were enrolled in the present study and a further 30 patients that underwent nephrectomy following trauma were selected as the control group. Immunohistochemical staining with HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB expression in the renal tissues, and western blot analysis were used to measure the relative expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to estimate the relative expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB mRNA. Statistical analysis was used to calculate the association between HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB expression and CAN grade. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB had markedly positive expression rates in renal tubular epithelial cell cytoplasm and membranes in CAN renal tissues, and the positive rates of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB increased with the aggravation of CAN pathological grade (I, II and III). The results of western blot analysis indicated that the expression levels of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB were significantly higher in the CAN group, compared with the normal group (P<0.05), and the expression levels increased with the progression of CAN grade. A positive association among HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB expression was identified. RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that the expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB mRNA in the CAN group was significantly higher than in the normal group (P<0.05), and the relative expression level of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB mRNA not only increased with the aggravation of CAN grade, but was also positively associated with the expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB, respectively. The abnormal expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB is therefore, an important manifestation of CAN and the expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB mRNA in the renal tissues are significantly associated with CAN pathological progression. HMGB1, TGF-β1 and NF-κB may form a signaling pathway that leads to the occurrence of CAN, which induces renal interstitial fibrosis.
Keywords: chronic allograft nephropathy; high mobility group protein B1; kidney transplant; nuclear factor-κB; transforming growth factor-β1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miR-627/HMGB1/NF-κB regulatory loop modulates TGF-β1-induced pulmonary fibrosis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):2983-2993. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27038. Epub 2018 Dec 9. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30536600
-
Liuweiwuling tablets attenuate BDL-induced hepatic fibrosis via modulation of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:232-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28864168
-
Staphylococcus aureus induces TGF-β1 and bFGF expression through the activation of AP-1 and NF-κB transcription factors in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Microb Pathog. 2018 Apr;117:276-284. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.02.024. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29452196
-
Anti-renal fibrosis effect of asperulosidic acid via TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction.Phytomedicine. 2019 Feb;53:274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668407
-
Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:670-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518614 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling Progressive Fibrosis with Pluripotent Stem Cells Identifies an Anti-fibrotic Small Molecule.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 10;29(11):3488-3505.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.019. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31825831 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines in Lung Transplantation.Lung. 2022 Dec;200(6):793-806. doi: 10.1007/s00408-022-00588-1. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Lung. 2022. PMID: 36348053 Review.
-
Extracellular HMGB1 Contributes to the Chronic Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy/Fibrosis by Modulating TGF-β1 Signaling.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 10;12:641973. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.641973. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33777037 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
