Targeting microRNA/UHRF1 pathways as a novel strategy for cancer therapy
- PMID: 29285183
- PMCID: PMC5738699
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.7290
Targeting microRNA/UHRF1 pathways as a novel strategy for cancer therapy
Abstract
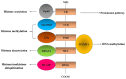
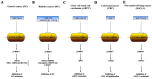
Ubiquitin-like containing plant homeodomain and RING finger domains 1 (UHRF1) is an anti-apoptotic protein involved in the silencing of several tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) through epigenetic modifications including DNA methylation and histone post-translational alterations, and also epigenetic-independent mechanisms. UHRF1 overexpression is observed in a number of solid tumors and hematological malignancies, and is considered a primary mechanism in inhibiting apoptosis. UHRF1 exerts its inhibitory activity on TSGs by binding to functional domains and therefore influences several epigenetic actors including DNA methyltransferase, histone deacetylase 1, histone acetyltransferase Tat-interacting protein 60 and histone methyltransferases G9a and Suv39H1. UHRF1 is considered to control a large macromolecular protein complex termed epigenetic code replication machinery, in order to maintain epigenetic silencing of TSGs during cell division, thus enabling cancer cells to escape apoptosis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are able to regulate the expression of its target gene by functioning as either an oncogene or a tumor suppressor. In the present review, the role of tumor suppressive miRNAs in the regulation of UHRF1, and the importance of targeting the microRNA/UHRF1 pathways in order to induce the reactivation of silenced TSGs and subsequent apoptosis are discussed.
Keywords: DNA methylation; apoptosis; cancer; epigenetics; microRNA; tumor suppressor genes; ubiquitin-like with PHD and RING finger domains 1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signalling pathways in UHRF1-dependent regulation of tumor suppressor genes in cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 14;35(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0453-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27839516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone Is a Multitarget Single Epidrug That Inhibits the UHRF1 Protein Complex.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;12(5):622. doi: 10.3390/genes12050622. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of UHRF1, associated with re-expression of tumor suppressor genes, is a common feature of natural compounds exhibiting anti-cancer properties.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 15;30(1):41. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-41. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21496237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic mechanism and target therapy of UHRF1 protein complex in malignancies.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jan 11;12:549-559. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S192234. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30666134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone-Induced Reactivation of Tumor Suppressor Genes in Cancer Cells Involves Epigenetic Mechanisms.Epigenet Insights. 2019 Apr 4;12:2516865719839011. doi: 10.1177/2516865719839011. eCollection 2019. Epigenet Insights. 2019. PMID: 31058255 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Thymoquinone and Difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) Synergistically Induce Apoptosis of Human Acute T Lymphoblastic Leukemia Jurkat Cells Through the Modulation of Epigenetic Pathways.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820947489. doi: 10.1177/1533033820947489. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32912061 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-506 Targets UHRF1 to Inhibit Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Invasion via the KISS1/PI3K/NF-κB Signaling Axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Nov 15;7:266. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00266. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31803739 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of post-translational modifications of UHRF1 in cancer.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024 May 9;17(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00540-y. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024. PMID: 38725075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HAUSP Is a Key Epigenetic Regulator of the Chromatin Effector Proteins.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 24;13(1):42. doi: 10.3390/genes13010042. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated Dialogue between UHRF1 and DNMT1 to Ensure Faithful Inheritance of Methylated DNA Patterns.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 18;10(1):65. doi: 10.3390/genes10010065. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30669400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Achour M, Jacq X, Rondé P, Alhosin M, Charlot C, Chataigneau T, Jeanblanc M, Macaluso M, Giordano A, Hughes AD, et al. The interaction of the SRA domain of ICBP90 with a novel domain of DNMT1 is involved in the regulation of VEGF gene expression. Oncogene. 2008;27:2187–2197. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210855. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berkyurek AC, Suetake I, Arita K, Takeshita K, Nakagawa A, Shirakawa M, Tajima S. The DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1 directly interacts with the SET and RING finger-associated (SRA) domain of the multifunctional protein Uhrf1 to facilitate accession of the catalytic center to hemi-methylated DNA. J Biol Chemistry. 2014;289:379–386. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.523209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
