Function of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer resistance to chemotherapy
- PMID: 29285186
- PMCID: PMC5738696
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.7276
Function of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer resistance to chemotherapy
Abstract
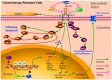
Drug resistance is a primary cause of chemotherapeutic failure; however, how this resistance develops is complex. A comprehensive understanding of chemotherapeutic resistance mechanisms may aid in identifying more effective drugs and improve the survival rates of patients with cancer. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R), a member of the insulin receptor family, has been extensively assessed for biological activity, and its putative contribution to tumor cell development and progression. Furthermore, researchers have attended to drugs that target IGF1R since IGF1R functions as a membrane receptor. However, how IGF1R participates in chemotherapeutic resistance remains unclear. Therefore, the present study described the IGF1R gene and its associated signaling pathways, and offered details of IGF1R-induced tumor chemoresistance associated with promoting cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter proteins and interactions with the extracellular matrix. The present study offered additional explanations for tumor chemotherapy resistance and provided a theoretical basis of IGF1R and its downstream pathways for future possible chemotherapy treatment options.
Keywords: cancer; chemotherapeutic resistance; insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; mechanisms; review.
Figures
References
-
- Hayashi Y, Asuzu DT, Gibbons SJ, Aarsvold KH, Bardsley MR, Lomberk GA, Mathison AJ, Kendrick ML, Shen KR, Taguchi T, et al. Membrane-to-nucleus signaling links insulin-like growth factor-1- and stem cell factor-activated pathways. PLoS One. 2013;8:e76822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076822. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
