Sulforaphane reverses gefitinib tolerance in human lung cancer cells via modulation of sonic hedgehog signaling
- PMID: 29285189
- PMCID: PMC5738694
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.7293
Sulforaphane reverses gefitinib tolerance in human lung cancer cells via modulation of sonic hedgehog signaling
Abstract
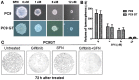
Gefitinib is a targeted anticancer drug that was developed as an effective clinical therapy for lung cancer. Numerous patients develop gefitinib resistance in response to treatment. Sulforaphane (SFN) is present in cruciferous vegetables, and has been demonstrated to inhibit the malignant growth of various types of cancer cells. To investigate the role of SFN in gefitinib resistance, a gefitinib-tolerant PC9 (PC9GT) cell model was established by continually exposing PC9 cells to gefitinib. Cell viability was measured using a cell proliferation assay. Components of the sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway and markers of lung cancer stem cells were detected via western blotting. SFN markedly inhibited the proliferation of PC9GT and PC9 cells in a dose-dependent manner; combination SFN/gefitinib treatment also markedly decreased PC9GT cell proliferation, compared with SFN or gefitinib administered alone (P<0.05). Western blot analysis revealed that the expression of SHH, Smoothened (SMO), zinc finger protein GLI1 (GLI1), GLI2, CD133 and CD44 were upregulated in PC9GT cells, as compared with in PC9 cells. Furthermore, SFN markedly inhibited the expression of SHH, SMO and GLI1 in PC9GT and PC9 cells in a dose dependent manner, and SFN combined with gefitinib markedly inhibited the expression of SHH, SMO, GLI1, CD133 and CD44 in PC9GT cells when compared with SFN or gefitinib monotherapy. The results of the present study demonstrated that SFN inhibits the proliferation of gefitinib-tolerant lung cancer cells via modulation of the SHH signaling pathway. Therefore, combined SFN and gefitinib therapy may be an effective approach for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: gefitinib tolerance; lung cancer; sonic hedgehog signaling pathway; sulforaphane.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sulforaphane inhibits self-renewal of lung cancer stem cells through the modulation of sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway and polyhomeotic homolog 3.AMB Express. 2021 Aug 23;11(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01281-x. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 34424425 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane regulates self-renewal of pancreatic cancer stem cells through the modulation of Sonic hedgehog-GLI pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Jan;373(1-2):217-27. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1493-6. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23129257
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling inhibition provides opportunities for targeted therapy by sulforaphane in regulating pancreatic cancer stem cell self-renewal.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046083. Epub 2012 Sep 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029396 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: Review of Smoothened and GLI Inhibitors.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Feb 15;8(2):22. doi: 10.3390/cancers8020022. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26891329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Jan;6(1):44-54. doi: 10.1039/b910196a. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20024066 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Involving the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway in Lung Cancer Therapy: Recent Advances.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 1;12:729088. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.729088. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35433472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Complex Interplay between Chronic Inflammation, the Microbiome, and Cancer: Understanding Disease Progression and What We Can Do to Prevent It.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 20;10(3):83. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030083. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29558443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary isothiocyanates and anticancer agents: exploring synergism for improved cancer management.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 11;11:1386083. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1386083. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38919393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple signaling pathways in the frontiers of lung cancer progression.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1593793. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593793. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Sulforaphane Potential as a Chemosensitizing Agent: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;16(2):244. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020244. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Puglisi M, Thavasu P, Stewart A, de Bono JS, O'Brien ME, Popat S, Bhosle J, Banerji U. AKT inhibition synergistically enhances growth-inhibitory effects of gefitinib and increases apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Lung Cancer. 2014;85:141–146. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ge X, Chen Q, Wu YP, Zhang Y, Xia H, Yuan D, Chen Q, Leng W, Chen L, Tang Q, et al. Induced IGF-1R activation contributes to gefitinib resistance following combined treatment with paclitaxel, cisplatin and gefitinib in A549 lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:1401–1408. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3331. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
