Dietary polyphenols influence antimetabolite agents: methotrexate, 6-mercaptopurine and 5-fluorouracil in leukemia cell lines
- PMID: 29285220
- PMCID: PMC5739607
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20501
Dietary polyphenols influence antimetabolite agents: methotrexate, 6-mercaptopurine and 5-fluorouracil in leukemia cell lines
Abstract
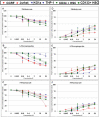
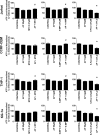
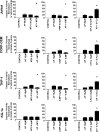
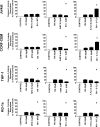
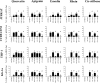
Polyphenols have been previously shown to sensitize leukemia cell lines to topoisomerase inhibitors. Here, we assess the effects of five polyphenols when used alone and in combination with antimetabolites: methotrexate, 6-mercaptopurine and 5-fluorouracil; in lymphoid and myeloid leukemia cells lines, and non-tumor control cells. The effects of combined treatments were investigated on ATP and glutathione levels, cell-cycle progression, DNA damage and apoptosis. Polyphenols antagonized methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine induced cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in most leukemia cell lines. This was associated with reduced DNA damage and increased glutathione levels, greater than that seen following individual treatments alone. In contrast, 5-fluorouracil when combined with quercetin, apigenin and rhein caused synergistic decrease in ATP levels, induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in some leukemia cell lines. However, antagonistic effects were observed when 5-fluorouracil was combined with rhein and cis-stilbene in myeloid cell lines. The effects were dependant on polyphenol type and chemotherapy agent investigated, and cell type treated. Interestingly treatment of non-tumor control cells with polyphenols protected cells from antimetabolite treatments. This suggests that polyphenols modulate the action of antimetabolite agents; more importantly they antagonized methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine actions, thus suggesting the requirement of polyphenol-exclusion during their use.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; 6-mercaptopurine; leukemia; methotrexate; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this submission.
Figures




References
-
- Leukemia and lymphoma Research Last accessed January 01 2017 at: http://leukemialymphomaresearch.org.uk/
-
- National Institute for Health Care Excellence (NICE) Last accessed March 06 2017 at: https://www.evidence.nhs.uk/Search?q=Antimetabolites.
-
- Food U.S, Drug Administration FDA. Last accessed March 2017 at: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/default.htm.
-
- American Cancer Society Last accessed January 2017 at: https://www.cancer.org/treatment.
-
- Cancer Research UK Last accessed January 01 2017 at: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/type/all/treatment.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

