Insulin receptor substrate-4 interacts with ubiquitin-specific protease 18 to activate the Jak/STAT signaling pathway
- PMID: 29285303
- PMCID: PMC5739690
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22510
Insulin receptor substrate-4 interacts with ubiquitin-specific protease 18 to activate the Jak/STAT signaling pathway
Abstract
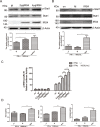
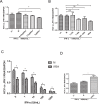
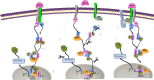
Ubiquitin-specific protease 18 (USP18) as a negative regulator of the Jak/STAT signaling pathway plays an important role in the host innate immune response. USP18 has been shown to bind to the type I interferon receptor subunit 2 (IFNAR2) to down-regulate the Jak/STAT signaling. In this study, we showed that insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-4 functioned as a novel USP18-binding protein. Co-precipitation assays revealed that two regions (amino acids 335-400 and 1094-1257) of IRS4 were related to bind to the C- terminal region of USP18. IRS4 binding to USP18 diminished the inhibitory effect of USP18 on Jak/STAT signaling. IRS4 over-expression enhanced while IRS4 knock-down suppressed the Jak/STAT signaling in the presence of IFN-a stimulation. As such, IRS4 increased IFN-a-mediated anti-HCV activity. Mechanistically, IRS4 promoted the IFN-a-induced Jak/STAT signaling by interact with USP18. These results suggested that IRS4 binds to USP18 to diminish the blunting effect of USP18 on IFN-a-induced Jak/STAT signaling. Our findings indicated that IRS4 is a novel USP18-binding protein that can be used to boost the host innate immunity to control HCV, and potentially other viruses that are sensitive to IFN-a.
Keywords: HCV; IRS4; Jak/STAT signaling pathway; USP18.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
USP18 Mediates Interferon Resistance of Dengue Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 30;12:682380. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.682380. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34017322 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin sensitizes the antiproliferative effect of interferon α/β by activation of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway signaling through protein kinase A-mediated inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in cancer cells.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):619-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.039. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24333668
-
ISG12a inhibits HCV replication and potentiates the anti-HCV activity of IFN-α through activation of the Jak/STAT signaling pathway independent of autophagy and apoptosis.Virus Res. 2017 Jan 2;227:231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.10.013. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27777077
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism(s) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) induced interferon resistance.Infect Genet Evol. 2013 Oct;19:113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23831932 Review.
-
The Jak-STAT pathway: cytokine signalling from the receptor to the nucleus.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 1999 Jan-Jul;19(1-4):75-120. doi: 10.3109/10799899909036638. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 1999. PMID: 10071751 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the early response to spinal cord injury identified a key role for mTORC1 signaling in the activation of neural stem progenitor cells.NPJ Regen Med. 2021 Oct 22;6(1):68. doi: 10.1038/s41536-021-00179-3. NPJ Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 34686684 Free PMC article.
-
USP18 is a significant driver of memory CD4 T-cell reduced viability caused by type I IFN signaling during primary HIV-1 infection.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Oct 28;15(10):e1008060. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008060. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31658294 Free PMC article.
-
The development of COVID-19 treatment.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 26;14:1125246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1125246. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive genomic analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant BA.2.76 in Jining City, China, 2022.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 17;25(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10246-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38632523 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization and whole-genome sequencing-based genetic analysis of influenza virus in Jining City during 2021-2022.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1196451. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1196451. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37426015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takaoka A, Yanai H. Interferon signalling network in innate defence. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:907–922. - PubMed
-
- Hwang SY, Hertzog PJ, Holland KA, Sumarsono SH, Tymms MJ, Hamilton JA, Whitty G, Bertoncello I, Kola I. A null mutation in the gene encoding a type I interferon receptor component eliminates antiproliferative and antiviral responses to interferons alpha and beta and alters macrophage responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:11284–11288. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muller U, Steinhoff U, Reis LF, Hemmi S, Pavlovic J, Zinkernagel RM, Aguet M. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 1994;264:1918–1921. - PubMed
-
- Swann JB, Hayakawa Y, Zerafa N, Sheehan KC, Scott B, Schreiber RD, Hertzog P, Smyth MJ. Type I IFN contributes to NK cell homeostasis, activation, and antitumor function. J Immunol. 2007;178:7540–7549. - PubMed
-
- de Veer MJ, Holko M, Frevel M, Walker E, Der S Paranjape JM, Silverman RH, Williams BRG. Functional classification of interferon-stimulated genes identified using microarrays. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:912. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

