Prognostic performance of combined use of high-sensitivity troponin T and creatine kinase MB isoenzyme in high cardiovascular risk patients with end-stage renal disease
- PMID: 29285428
- PMCID: PMC5743045
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.2017.36.4.358
Prognostic performance of combined use of high-sensitivity troponin T and creatine kinase MB isoenzyme in high cardiovascular risk patients with end-stage renal disease
Abstract
Background: The principal goal of this study was to determine the importance of high-sensitivity troponin T (hs-TnT) and creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB) in predicting cardiovascular events in asymptomatic end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients.
Methods: This study included 110 participants; 54 ESRD patients undergoing hemodialysis and 56 healthy control participants. Biochemical parameters and cardiac markers were estimated. Comparative utilities were assessed through logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses.
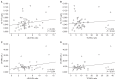
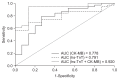
Results: We found that 96.3% of ESRD patients had an elevated level of hs-TnT (mean, 0.049 ± 0.0324 μg/L) compared to healthy participants. Among patients with ESRD, hs-TnT showed significant correlations with the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (P = 0.042, r = 0.278) and total cholesterol/HDL-C (P = 0.044, r = 0.276) ratios. CK-MB (odds ratio [OR], 1.138; P = 0.04) and hs-TnT (OR, 2.153; P = 0.017) predicted cardiovascular events on logistic regression analysis, and the prediction was improved by the model that combined two cardiac markers. The diagnostic performance of hs-TnT and CK-MB alone and the combination of the two biomarkers was assessed by the area under the ROC curve (AUC). The highest AUC was produced by the combination of hs-TnT and CK-MB markers (0.920) compared to hs-TnT or CK-MB alone.
Conclusion: In asymptomatic patients with ESRD, hs-TnT appeared to be an important predictor for cardiovascular mortality, and its diagnostic accuracy improved with CK-MB. This study provides new insights into the predictive value of multiple biomarkers for identifying cardiovascular events in ESRD patients on hemodialysis.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Creatine kinase MB isoenzyme; End-stage renal disease; High-sensitivity troponin T.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Weak diagnostic performance of troponin, creatine kinase and creatine kinase-MB to diagnose or exclude myocardial infarction after successful resuscitation.Int J Cardiol. 2014 May 1;173(2):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.02.033. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24636545
-
Prognostic value of troponin T, troponin I, and CK-MBmass in patients with chronic renal failure.Med Klin (Munich). 2003 Apr 15;98(4):188-92. doi: 10.1007/s00063-003-1243-3. Med Klin (Munich). 2003. PMID: 12715142
-
Prognostic Value of High-Sensitivity Versus Conventional Cardiac Troponin T Assays Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Jun;71(6):822-830. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.10.016. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29310884
-
Creatine kinase isoenzyme MB mass, cardiac troponin T, and myosin light chain isotype 1 as serological markers of myocardial injury and their prognostic importance in acute coronary syndrome.Dan Med Bull. 1998 Feb;45(1):34-50. Dan Med Bull. 1998. PMID: 9504265 Review.
-
Laboratory diagnosis of patients with acute chest pain.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2000 Mar;38(3):187-97. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2000.027. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2000. PMID: 10905753 Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T and Echocardiographic Parameters in Chronic Kidney Disease: Results From the KNOW-CKD Cohort Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 17;8(18):e013357. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013357. Epub 2019 Sep 13. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31514574 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes of prolonged dual antiplatelet therapy after coronary drug-eluting stent implantation in dialysis patients.Clin Kidney J. 2020 May 3;13(5):803-812. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa037. eCollection 2020 Oct. Clin Kidney J. 2020. PMID: 33125004 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Reclassification by a High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Assay.Ann Emerg Med. 2020 Nov;76(5):566-579. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2020.06.047. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Ann Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32807538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United States Renal Data System (USRDS) USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report: Atlas of End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD: 2009.
-
- Chijioke A, Makusidi AM, Shittu AO, et al. Pattern of lipid profile in dialysis naive chronic kidney disease patients from Ilorin, Nigeria. Internet J Nephrol. 2010;6:1–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

