Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral-flow dipstick assay for detection of bovine ephemeral fever virus
- PMID: 29288049
- PMCID: PMC7126596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcp.2017.12.003
Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral-flow dipstick assay for detection of bovine ephemeral fever virus
Abstract
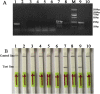
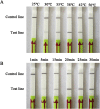
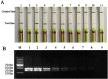
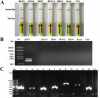
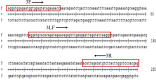
Bovine ephemeral fever virus (BEFV), identified as the causative pathogen of bovine ephemeral fever (BEF), is responsible for increasing numbers of epidemics/outbreaks and has a significant harmful effect on the livestock industry. Therefore, a rapid detection assay is imperative for BEFV diagnosis. In this study, we described the development of lateral-flow dipstick isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (LFD-RPA) assays for detection of BEFV. RPA primers and LF probes were designed by targeting the specific G gene, and the amplification product can be visualized on a simple lateral flow dipstick with the naked eyes. The amplification reaction was performed at 38 °C for 20 min and LFD incubation time within 5 min. The detection limit of this assay was 8 copies per reaction, and there was no cross-reactivity with other bovine infectious viruses such as bovine viral diarrhea virus, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus, bovine respiratory syncytial virus, bovine coronavirus, bovine parainfluenza virus type 3, bovine vesicular stomatitis virus. In addition, the assay was performed with total 128 clinical specimens and the diagnostic results were compared with conventional RT-PCR, real-time quantative(q) PCR. The result showed that the coincidence rate of BEFV LFD-RPA and real-time qPCR was 96.09% (123/128), which was higher than conventional RT-PCR. The RPA combined with LFD assay probably provides a rapid and sensitive alternative for diagnosis of BEFV infections outbreak.
Keywords: Bovine ephemeral fever virus (BEFV); Lateral flow dipstick; Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA).
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hsieh Y.C., Chen S.H., Chou C.C., Ting L.J., Itakura C., Wang F.I. Bovine ephemeral fever in Taiwan (2001-2002) J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2005;67(4):411–416. - PubMed
-
- Nandi S., Negi B.S. Bovine ephemeral fever: a review. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999;22(2):81–91. - PubMed
-
- Walker P.J. Bovine ephemeral fever in Australia and the world. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005;292:57–80. - PubMed
-
- Bai W.B., Jiang C.L., Davis S.S. Preliminary observations on the epidemiology of bovine ephemeral fever in China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1991;23(1):22–26. - PubMed
-
- Li Z., Zheng F., Gao S., Wang S., Wang J., Liu Z., Du J., Yin H. Large-scale serological survey of bovine ephemeral fever in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2015;176(1–2):155–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

