Third-generation oncolytic herpes simplex virus inhibits the growth of liver tumors in mice
- PMID: 29288515
- PMCID: PMC5834814
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13492
Third-generation oncolytic herpes simplex virus inhibits the growth of liver tumors in mice
Abstract
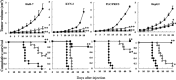
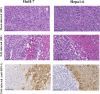
Multimodality therapies are used to manage patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), although advanced HCC is incurable. Oncolytic virus therapy is probably the next major breakthrough in cancer treatment. The third-generation oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) T-01 kills tumor cells without damaging the surrounding normal tissues. Here we investigated the antitumor effects of T-01 on HCC and the host's immune response to HCC cells. The cytopathic activities of T-01 were tested in 14 human and 1 murine hepatoma cell line in vitro. In various mouse xenograft models, HuH-7, KYN-2, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 human cells and Hepa1-6 murine cells were used to investigate the in vivo efficacy of T-01. T-01 was cytotoxic to 13 cell lines (in vitro). In mouse xenograft models of subcutaneous, orthotopic and peritoneal tumor metastasis in athymic mice (BALB/c nu/nu), the growth of tumors formed by the human HCC cell lines and hepatoblastoma cell line was inhibited by T-01 compared with that of mock-inoculated tumors. In a bilateral Hepa1-6 subcutaneous tumor model in C57BL/6 mice, the growth of tumors inoculated with T-01 was inhibited, as was the case for contralateral tumors. T-01 also significantly reduced tumor growth. T-01 infection significantly enhanced antitumor efficacy via T cell-mediated immune responses. Results demonstrate that a third-generation oncolytic HSV-1 may serve as a novel treatment for patients with HCC.
Keywords: antitumor immunity; herpes simplex virus; human hepatocellular carcinoma; oncolytic immunotherapy; oncolytic virus.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A hepatocellular carcinoma-specific adenovirus variant, CV890, eliminates distant human liver tumors in combination with doxorubicin.Cancer Res. 2001 Sep 1;61(17):6428-36. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11522637
-
Oncolytic herpes viral therapy is effective in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.J Gastrointest Surg. 2006 Apr;10(4):532-42. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2005.08.036. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006. PMID: 16627219 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Editing of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Enables Interferon Induction and Viral Replication That Destroy Malignant Cells.J Virol. 2019 Jan 4;93(2):e01761-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01761-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30404809 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic virus therapy using genetically engineered herpes simplex viruses.Hum Cell. 2002 Sep;15(3):151-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-0774.2002.tb00109.x. Hum Cell. 2002. PMID: 12703545 Review.
-
The Current Landscape of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Viruses as Novel Therapies for Brain Malignancies.Viruses. 2021 Jun 17;13(6):1158. doi: 10.3390/v13061158. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34204248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of a third-generation oncolytic herpes simplex virus in refractory soft tissue sarcoma xenograft models.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022 Apr 26;25:225-235. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.04.010. eCollection 2022 Jun 16. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022. PMID: 35615265 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic virus-based hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Current status, intravenous delivery strategies, and emerging combination therapeutic solutions.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Jan;18(1):100771. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.100771. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 36896445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive assessment on the applications of oncolytic viruses for cancer immunotherapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1082797. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1082797. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36569326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of a third-generation oncolytic herpes virus G47Δ in models of human esophageal carcinoma.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Oct 30;23:402-411. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.10.012. eCollection 2021 Dec 17. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 34853811 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Glioblastoma: The Current State of Different Therapeutic Approaches.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(10):1701-1715. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210113152108. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33441071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arzumanyan A, Reis HMGPV, Feitelson MA. Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV‐ and HCV‐associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:123‐135. - PubMed
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5‐S16. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Raoul JL, Sherman M, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: subanalyses of a phase III trial. J Hepatol. 2012;57:821‐829. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

