Interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes prostate cancer resistance to androgen deprivation therapy via regulating pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 expression
- PMID: 29288516
- PMCID: PMC5834804
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13493
Interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes prostate cancer resistance to androgen deprivation therapy via regulating pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 expression
Abstract
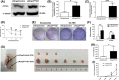
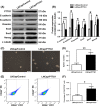
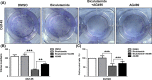
Prostate cancer can progress from androgen dependence to androgen deprivation resistance with some unknown mechanisms. The current study aims to explore the possible role of pituitary tumor transforming gene1 (PTTG1) in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Initially, we found that PTTG1 expression was significantly increased in androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines PC3, DU145 and CRPC specimens compared with that in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cell line LNCaP and initial prostate cancer specimens. PTTG1 overexpression significantly enhanced the cell survival rate, clonality and tumorigenicity in LNCaP cells upon androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT). While knockdown of PTTG1 expression significantly elevated the sensitivity of DU145 cells to ADT. The effects of PTTG1 overexpression on LNCaP cells may be ascribed to the induced EMT and increased CD44+ CD24- cancer stem cell population. Furthermore, we detected that PTTG1 expression was regulated by interleukin-6 via activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) directly binding to the region -500 to +1 of PTTG1 promoter in LNCaP cells. In conclusion, our results elucidate that interleukin-6/STAT3 activation can increase PTTG1 expression and, consequently, promote the resistance to ADT in CRPC by inducing EMT and increasing the cancer stem cell population, suggesting that PTTG1 may be a novel therapeutic target for CRPC.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; castration-resistant prostate cancer; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; interleukin-6; pituitary tumor transforming gene 1.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69‐90. - PubMed
-
- Patel LR, Barton MC. TRIM‐ing ligand dependence in castration‐resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:776‐778. - PubMed
-
- Pei L, Melmed S. Isolation and characterization of a pituitary tumor‐transforming gene (PTTG). Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:433‐441. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

