Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns Derived From the Extracellular Matrix Provide Temporal Control of Innate Immunity
- PMID: 29290139
- PMCID: PMC5958376
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155417740880
Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns Derived From the Extracellular Matrix Provide Temporal Control of Innate Immunity
Abstract
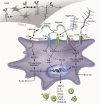
It is evident that components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) act as danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) through direct interactions with pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) including Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and inflammasomes. Through these interactions, ECM-derived DAMPs autonomously trigger sterile inflammation or prolong pathogen-induced responses through the production of proinflammatory mediators and the recruitment of leukocytes to sites of injury and infection. Recent research, however, suggests that ECM-derived DAMPs are additionally involved in the resolution and fine-tuning of inflammation by orchestrating the production of anti-inflammatory mediators that are required for the resolution of tissue inflammation and the transition to acquired immunity. Thus, in this review, we discuss the current knowledge of the interplay between ECM-derived DAMPs and the innate immune signaling pathways that are activated to provide temporal control of innate immunity.
Keywords: Toll-like receptors (TLRs); biglycan; decorin; extracellular matrix; hyaluronan; inflammasome; inflammation; innate immunity; versican.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sorokin L. The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(10):712–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

