Relation of the IGF/IGF1R system to autophagy in colitis and colorectal cancer
- PMID: 29290648
- PMCID: PMC5739918
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8109
Relation of the IGF/IGF1R system to autophagy in colitis and colorectal cancer
Abstract
Metabolic syndrome (MetS), as a chronic inflammatory disorder has a potential role in the development of inflammatory and cancerous complications of the colonic tissue. The interaction of DNA damage and inflammation is affected by the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) signaling pathway. The IGF1R pathway has been reported to regulate autophagy, as well, but sometimes through a bidirectional context. Targeting the IGF1R-autophagy crosstalk could represent a promising strategy for the development of new antiinflammatory and anticancer therapies, and may help for subjects suffering from MetS who are at increased risk of colorectal cancer. However, therapeutic responses to targeted therapies are often shortlived, since a signaling crosstalk of IGF1R with other receptor tyrosine kinases or autophagy exists, leading to acquired cellular resistance to therapy. From a pharmacological point of view, it is attractive to speculate that synergistic benefits could be achieved by inhibition of one of the key effectors of the IGF1R pathway, in parallel with the pharmacological stimulation of the autophagy machinery, but cautiousness is also required, because pharmacologic IGF1R modulation can initiate additional, sometimes unfavorable biologic effects.
Keywords: Autophagy; Colitis; Colorectal cancer; IGF1R; Insulin-like growth factor; Metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No conflict of interest.
Figures
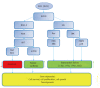
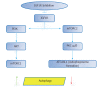
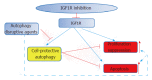
References
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Sipos F, Galamb O, Herszényi L, Molnár B, Solymosi N, Zágoni T, Berczi L, Tulassay Z. Elevated insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, hepatocyte growth factor receptor and telomerase protein expression in mild ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:289–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

