Engineered Microenvironments for Maturation of Stem Cell Derived Cardiac Myocytes
- PMID: 29290797
- PMCID: PMC5743464
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.19441
Engineered Microenvironments for Maturation of Stem Cell Derived Cardiac Myocytes
Abstract
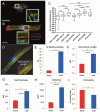
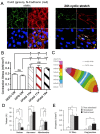
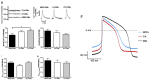
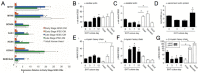
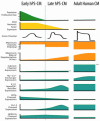
Through the use of stem cell-derived cardiac myocytes, tissue-engineered human myocardial constructs are poised for modeling normal and diseased physiology of the heart, as well as discovery of novel drugs and therapeutic targets in a human relevant manner. This review highlights the recent bioengineering efforts to recapitulate microenvironmental cues to further the maturation state of newly differentiated cardiac myocytes. These techniques include long-term culture, co-culture, exposure to mechanical stimuli, 3D culture, cell-matrix interactions, and electrical stimulation. Each of these methods has produced various degrees of maturation; however, a standardized measure for cardiomyocyte maturation is not yet widely accepted by the scientific community.
Keywords: Cardiac Myocytes; Differentiation; Maturation; Stem cells; Tissue Engineering..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Braam SR, Tertoolen L, van de Stolpe A, Meyer T, Passier R, Mummery CL. Prediction of drug-induced cardiotoxicity using human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4:107–16. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M. et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

