Factors delaying management of acute stroke: An Indian scenario
- PMID: 29291175
- PMCID: PMC5737064
- DOI: 10.4103/IJCIIS.IJCIIS_20_17
Factors delaying management of acute stroke: An Indian scenario
Abstract
Background and purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess factors causing delay in treatment of acute stroke in a tertiary care institute in South India.
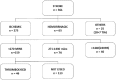
Methods: All clinically suspected cases of acute stroke presenting to the emergency department over a period of 1 year were prospectively followed up and data collected as per a preset pro forma. The various time intervals from stroke onset to definitive management and other pertinent data were collected. The time delays have been evaluated in the decision tree model: Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detection. Significance was assessed at 5% level of significance (P < 0.05).
Results: The mean prehospital time delay for all clinically suspected stroke (n = 361) in our institute was 716 min and the median time 190 min. The mean total in-hospital delay was 94.17 ± 54.5 min and median time being 82 min. The onset of symptoms to first medical contact was the main interval that influenced the prehospital delay. Computed tomographic (CT) diagnosis to stroke unit admission influenced the in-hospital delay the most.
Conclusions: Lack of awareness regarding stroke leads to delayed seeking of treatment for the same. The factors that contribute to the in-hospital delay included patient admission procedure delay, lack of staff to transport the patient, and the distance between the stroke unit and CT room. Educating the community with regard to "stroke" and implementation of a better pre- and in-hospital stroke care system is a need of the hour in the country.
Keywords: Decision tree analysis; in-hospital; prehospital; stroke; thrombolysis; time delays.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ropper AH, Samuels MA. Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology. 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2014.
-
- Bhaumik S. India launches stroke registry to combat “epidemic”. BMJ. 2013;346:f223. - PubMed
-
- Pandian JD, Kalra G, Jaison A, Deepak SS, Shamsher S, Singh Y, et al. Knowledge of stroke among stroke patients and their relatives in Northwest India. Neurol India. 2006;54:152–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

