Overactive bladder symptom severity, bother, help-seeking behavior, and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes: a path analysis
- PMID: 29291738
- PMCID: PMC5749008
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-017-0829-z
Overactive bladder symptom severity, bother, help-seeking behavior, and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes: a path analysis
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the relationships among overactive bladder (OAB) symptom severity, bother, help-seeking behavior, and quality of life (QOL) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: A total of 127 diabetic patients, aged at least 18 years, with overactive bladder from a hospital in Shandong Province, China, were recruited for this study. Symptom severity, bother, and quality of life were assessed using the Overactive Bladder Symptom Score (OABSS), Patient Perception of Bladder Condition (PPBC), and Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short Form (OAB-q SF), respectively. Help-seeking behavior was assessed by asking patients whether they consulted health care professionals or received treatment for their bladder problems. A two-step path analysis was performed to analyze the data.
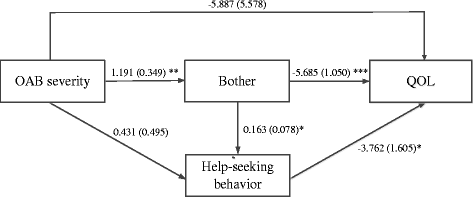
Results: OAB symptom severity was directly associated with lower levels of QOL, and the strength of this association was no longer significant when taking bother and help-seeking behavior into account. Bother increased with OAB symptom severity, and patients with bothersome OAB tended to have lower levels of QOL. Moreover, bother increased help-seeking behavior; however, patients who sought help tended to have lower levels of QOL.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the role of bother and help-seeking behavior in the relationship between OAB symptom severity and QOL. To improve a patient's QOL, health care providers should focus not only on symptom bother but also on dysfunctional help-seeking patterns.
Keywords: Bother; Help-seeking behavior; Overactive bladder; Quality of life; Symptom severity.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Shandong University. All patients provided informed consent before the survey.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of symptom bother and health-related quality of life in Japanese female patients with overactive bladder.Neurourol Urodyn. 2015 Nov;34(8):730-5. doi: 10.1002/nau.22663. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015. PMID: 25212503
-
Symptom severity and patient perceptions in overactive bladder: how are they related?BJU Int. 2009 Oct;104(7):968-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08498.x. Epub 2009 Mar 10. BJU Int. 2009. PMID: 19338560
-
The impact of overactive bladder on mental health, work productivity and health-related quality of life in the UK and Sweden: results from EpiLUTS.BJU Int. 2011 Nov;108(9):1459-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.10013.x. Epub 2011 Mar 3. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21371240
-
Patient-reported outcomes and different approaches to urinary parameters in overactive bladder: what should we measure?Int Urogynecol J. 2012 Feb;23(2):179-92. doi: 10.1007/s00192-011-1526-9. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Int Urogynecol J. 2012. PMID: 22011932 Review.
-
Overactive bladder patients and role of the pharmacist.J Am Pharm Assoc (Wash). 2002 May-Jun;42(3):469-76; quiz 477-8. doi: 10.1331/108658002763316905. J Am Pharm Assoc (Wash). 2002. PMID: 12030634 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilizing Bladder Diaries to Prevent Unnecessary Treatment in Patients With Storage Dysfunction: A Retrospective Study.Cureus. 2024 Sep 2;16(9):e68437. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68437. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39360064 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of exercise and/or nutritional interventions to improve the quality of life of women with breast cancer receiving radiation therapy: a scoping review.Support Care Cancer. 2024 Oct 23;32(11):745. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08933-1. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39441426 Free PMC article.
-
Global Trends in Studies on the Presence of Demodex spp. in Patients Diagnosed with Blepharitis.J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2024 Jun 30;18(2):84-93. doi: 10.18502/jad.v18i2.17531. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2024. PMID: 39850258 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of coated flow diverters in the treatment of cerebral aneurysms during single antiplatelet therapy: A multicenter study.Interv Neuroradiol. 2024 Dec;30(6):819-826. doi: 10.1177/15910199241286542. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Interv Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 39360399 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life for patients on oncology treatments in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: a systematic review.J Pharm Policy Pract. 2025 Jan 13;18(1):2449036. doi: 10.1080/20523211.2024.2449036. eCollection 2025. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2025. PMID: 39811823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haylen BT, de Ridder D, Freeman RM, Swift SE, Berghmans B, Lee J, et al. An international Urogynecological association (IUGA)/international continence society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29:4–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

